Explore: Electromechanical Clutches
Discover books, insights, and more — all in one place.
Learn more about Electromechanical Clutches with top reads curated from trusted sources — all in one place.
AI-Generated Overview About “electromechanical-clutches”:
Books Results
Source: The Open Library
The Open Library Search Results
Search results from The Open Library
1Manual of Electromechanical Devices
By Douglas C. Greenwood
“Manual of Electromechanical Devices” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Manual of Electromechanical Devices
- Author: Douglas C. Greenwood
- Language: English
- Number of Pages: Median: 337
- Publisher: McGraw Hill Book Company
- Publish Date: 1965
- Publish Location: New York, USA
“Manual of Electromechanical Devices” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ electromechanical - mechanics - engineering - electronics - electromagnets - solenoids - relays - special-purpose electric motors - servos - synchros - switches - electromechanical clutches - brake speed reducers
Edition Identifiers:
- The Open Library ID: OL26244918M
- Library of Congress Control Number (LCCN): 64022192
Access and General Info:
- First Year Published: 1965
- Is Full Text Available: No
- Is The Book Public: No
- Access Status: No_ebook
Online Access
Downloads Are Not Available:
The book is not public therefore the download links will not allow the download of the entire book, however, borrowing the book online is available.
Online Borrowing:
Online Marketplaces
Find Manual of Electromechanical Devices at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
Wiki
Source: Wikipedia
Wikipedia Results
Search Results from Wikipedia
Semi-automatic transmission
from hydraulic, pneumatic, and electromechanical clutches to vacuum-operated, electromagnetic, and even centrifugal clutches. Fluid couplings (most commonly
Electromagnetic brake
Electromagnetic brakes or EM brakes are used to slow or stop vehicles using electromagnetic force to apply magnetic resistance through induction or mechanical
Harvard Mark I
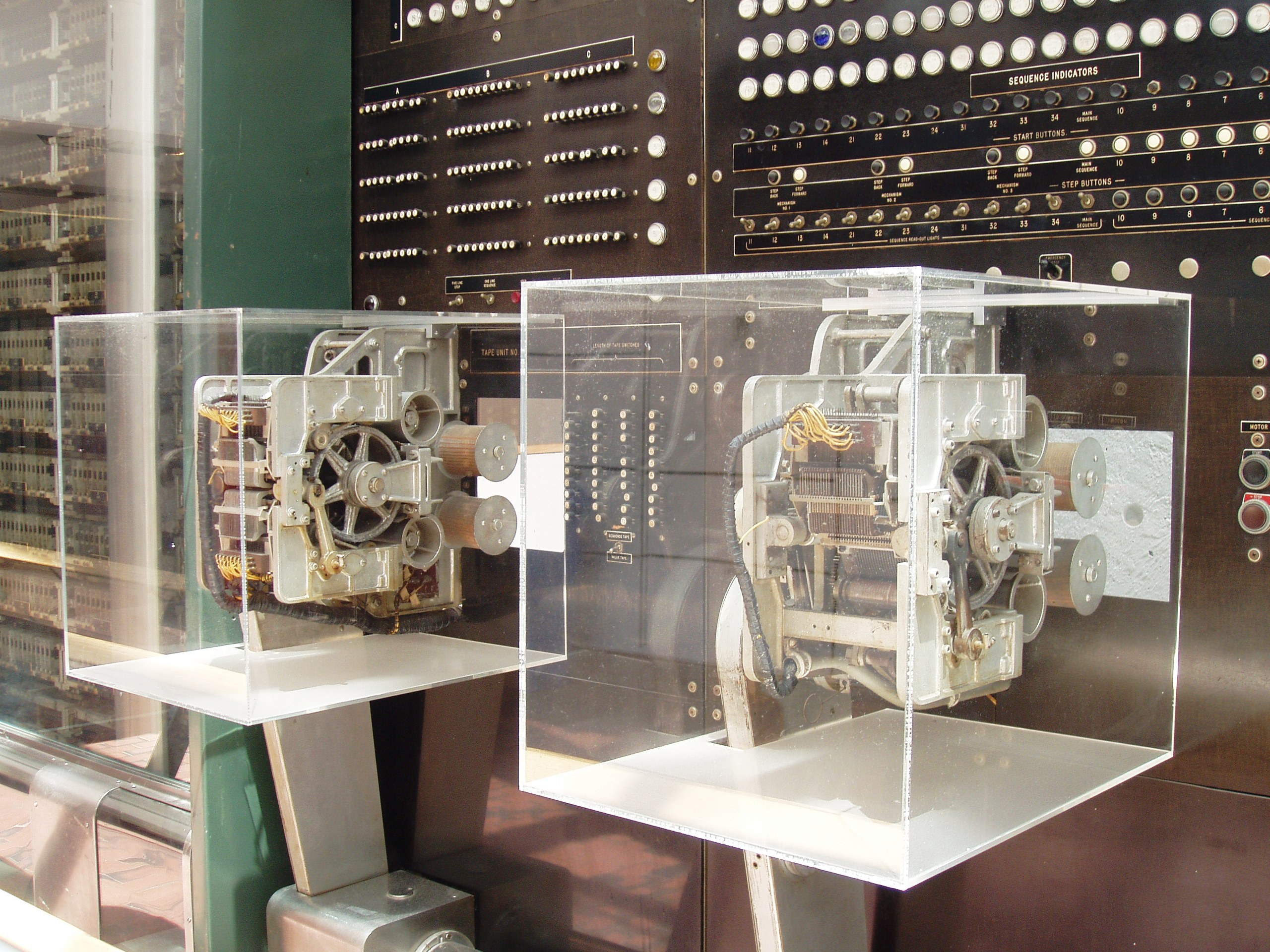
was built from switches, relays, rotating shafts, and clutches. It used 765,000 electromechanical components and hundreds of miles of wire, comprising
Torsional vibration
electromechanical drive system, Vibrations in Physical Systems, ISSN 0860-6897, Vol.27, pp.187-194, 2016 Konowrocki R., Analysis of electromechanical
ZF Friedrichshafen
complete front and rear axles, passive and semi-active dampers, and electromechanical active chassis systems. Sales (2020): €8,459 million. Products: Automatic
Mercedes-Benz CLA

sports suspension with independently developed front and rear axles, electromechanical AMG speed-sensitive sports steering, AMG high-performance braking
Delay box
charging scheme to trigger a unijunction transistor to release an electromechanical relay. Such drag racing delay timers are very crude by today's standards
Magnetic gear
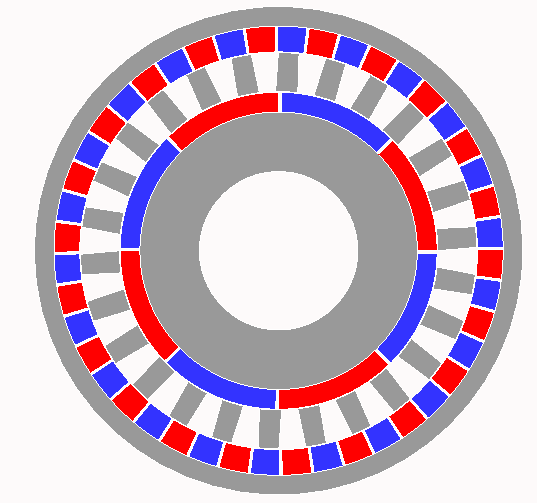
Nos. 7–8, p. 362-65 Furlani, E. P., 2001, “Permanent Magnet and Electromechanical Devices”, Academic Press, San Diego. Lorimer, W., Hartman, A., 1997
Mercedes-Benz E-Class (W210)

the system was totally redesigned and simplified. Rather than using the clutches and couplings of the earlier design, Mercedes opted to use three open differentials:
Karsten Stahl
components such as gears, synchronizers, multi-plate clutches, rolling-element bearings and electromechanical drivetrain systems. Stahl is a member of several