Explore: Index Inversés
Discover books, insights, and more — all in one place.
Learn more about Index Inversés with top reads curated from trusted sources — all in one place.
AI-Generated Overview About “index-invers%C3%A9s”:
Books Results
Source: The Open Library
The Open Library Search Results
Search results from The Open Library
1International Acronyms, Initialisms, & Abbreviations Dictionary
By Ellen T. Crowley

“International Acronyms, Initialisms, & Abbreviations Dictionary” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ International Acronyms, Initialisms, & Abbreviations Dictionary
- Author: Ellen T. Crowley
- Language: English
- Number of Pages: Median: 950
- Publisher: Gale Group - Gale Research Co.
- Publish Date: 1985
- Publish Location: Detroit, Mich
- Dewey Decimal Classification:
- Library of Congress Classification: P--0365.00000000.I57 1984
“International Acronyms, Initialisms, & Abbreviations Dictionary” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ Abbreviations - Dictionaries - Acronyms - Sigles - Anglais (Langue) - Index inversés - Abréviations
Edition Identifiers:
- The Open Library ID: OL17910857M - OL11317263M
- Online Computer Library Center (OCLC) ID: 10985449
- All ISBNs: 9780810305090 - 0810305097
Book Classifications
- Library of Congress Classification (LCC): ➤ ❛P--0365.00000000.I57 1984❜.
Access and General Info:
- First Year Published: 1985
- Is Full Text Available: Yes
- Is The Book Public: No
- Access Status: Borrowable
Online Access
Downloads Are Not Available:
The book is not public therefore the download links will not allow the download of the entire book, however, borrowing the book online is available.
Online Borrowing:
- Borrowing from Open Library: Borrowing link
- Borrowing from Archive.org: Borrowing link
Online Marketplaces
Find International Acronyms, Initialisms, & Abbreviations Dictionary at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
Wiki
Source: Wikipedia
Wikipedia Results
Search Results from Wikipedia
Inverted index
computer science, an inverted index (also referred to as a postings list, postings file, or inverted file) is a database index storing a mapping from content
Herfindahl–Hirschman index
Simpson diversity index, which is a diversity index used in ecology; the inverse participation ratio (IPR) in physics; and the inverse of the effective
Corruption Perceptions Index
The Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) is an index that scores and ranks countries by their perceived levels of public sector corruption, as assessed
S&P 500

trillion as of August 29, 2025. The S&P 500 index is a public float weighted/capitalization-weighted index. The ten largest companies on the list of S&P
Diversity index
indices have been the inverse Simpson index (1/λ) and the Gini–Simpson index (1 − λ). Both of these have also been called the Simpson index in the ecological
Hang Seng Index
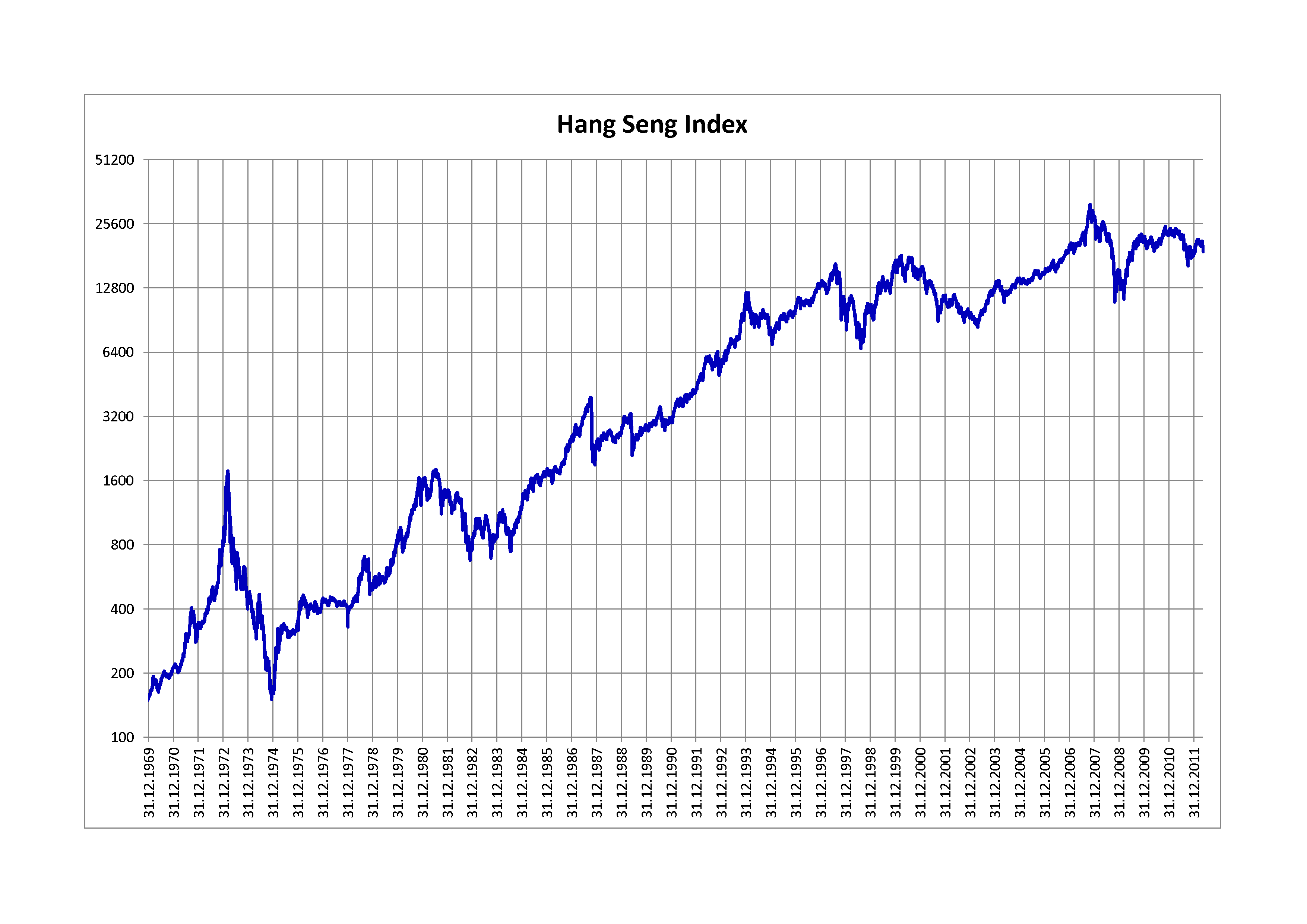
The Hang Seng Index (HSI) is a market-capitalisation-weighted stock market index in Hong Kong adjusted for free float. It tracks and records daily changes
Body mass index

Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms (kg) and height in metres (m). The BMI may be determined first by measuring its components by means of a weighing scale and a stadiometer. The multiplication and division may be carried out directly, by hand or using a calculator, or indirectly using a lookup table (or chart). The table displays BMI as a function of mass and height and may show other units of measurement (converted to metric units for the calculation). The table may also show contour lines or colours for different BMI categories. The BMI is a convenient rule of thumb used to broadly categorize a person as based on tissue mass (muscle, fat, and bone) and height. Major adult BMI classifications are underweight (under 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5 to 24.9), overweight (25 to 29.9), and obese (30 or more). When used to predict an individual's health, rather than as a statistical measurement for groups, the BMI has limitations that can make it less useful than some of the alternatives, especially when applied to individuals with abdominal obesity, short stature, or high muscle mass. BMIs under 20 and over 25 have been associated with higher all-cause mortality, with the risk increasing with distance from the 20–25 range.
Drazin inverse
mathematics, the Drazin inverse, named after Michael P. Drazin, is a kind of generalized inverse of a matrix. Let A be a square matrix. The index of A is the least
Refractive index

In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2, where θ1 and θ2 are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices n1 and n2. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n {\displaystyle n} , can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is v = c/n, and similarly the wavelength in that medium is λ = λ0/n, where λ0 is the wavelength of that light in vacuum. This implies that vacuum has a refractive index of 1, and assumes that the frequency (f = v/λ) of the wave is not affected by the refractive index. The refractive index may vary with wavelength. This causes white light to split into constituent colors when refracted. This is called dispersion. This effect can be observed in prisms and rainbows, and as chromatic aberration in lenses. Light propagation in absorbing materials can be described using a complex-valued refractive index. The imaginary part then handles the attenuation, while the real part accounts for refraction. For most materials the refractive index changes with wavelength by several percent across the visible spectrum. Consequently, refractive indices for materials reported using a single value for n must specify the wavelength used in the measurement. The concept of refractive index applies across the full electromagnetic spectrum, from X-rays to radio waves. It can also be applied to wave phenomena such as sound. In this case, the speed of sound is used instead of that of light, and a reference medium other than vacuum must be chosen. Refraction also occurs in oceans when light passes into the halocline where salinity has impacted the density of the water column. For lenses (such as eye glasses), a lens made from a high refractive index material will be thinner, and hence lighter, than a conventional lens with a lower refractive index. Such lenses are generally more expensive to manufacture than conventional ones.
Stock market index
In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures the performance of a stock market, or of a subset of a stock market. It helps