Downloads & Free Reading Options - Results
Generation Text by Michael M. Osit
Read "Generation Text" by Michael M. Osit through these free online access and download options.
Books Results
Source: The Internet Archive
The internet Archive Search Results
Available books for downloads and borrow from The internet Archive
1ERIC EJ812645: NaturalReader: A New Generation Text Reader
By ERIC
NaturalReader (http://www.naturalreaders.com/) is a new generation text reader, which means that it reads any machine readable text using synthesized speech without having to copy and paste the selected text into the NaturalReader application window. It installs a toolbar directly into all of the Microsoft Office[TM] programs and uses a mini-board to read text in other applications such as Adobe 7[TM]. The Neospeech[TM] voices which are available with the product are the most natural sounding synthetic voices that this reviewer has heard. The software has numerous additional enhancements which make it a program with universal design appeal. Overall this product exceeded most of the expectations for an electronic text reader and provided exceptional value for the low purchase price.
“ERIC EJ812645: NaturalReader: A New Generation Text Reader” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ ERIC EJ812645: NaturalReader: A New Generation Text Reader
- Author: ERIC
- Language: English
“ERIC EJ812645: NaturalReader: A New Generation Text Reader” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ ERIC Archive - Computer Software Evaluation - Computer Software Reviews - Computational Linguistics - Language Processing - Assistive Technology - Accessibility (for Disabled) - Reading Improvement - Foreign Countries - Flood, Jacqueline
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ERIC_EJ812645
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 6.28 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 226 times, the file-s went public at Fri May 27 2016.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Animated GIF - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find ERIC EJ812645: NaturalReader: A New Generation Text Reader at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
2Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-27_06-13-21
By oobabooga
A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Supports transformers, GPTQ, llama.cpp (ggml/gguf), Llama models. Text generation web UI A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Its goal is to become the AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui of text generation. | | ||:---:|:---:|| | | Features 3 interface modes: default (two columns), notebook, and chat Multiple model backends: transformers , llama.cpp , ExLlama , AutoGPTQ , GPTQ-for-LLaMa , ctransformers Dropdown menu for quickly switching between different models LoRA: load and unload LoRAs on the fly, train a new LoRA using QLoRA Precise instruction templates for chat mode, including Llama-2-chat, Alpaca, Vicuna, WizardLM, StableLM, and many others 4-bit, 8-bit, and CPU inference through the transformers library Use llama.cpp models with transformers samplers ( llamacpp_HF loader) Multimodal pipelines, including LLaVA and MiniGPT-4 Extensions framework Custom chat characters Very efficient text streaming Markdown output with LaTeX rendering, to use for instance with GALACTICA API, including endpoints for websocket streaming ( see the examples ) To learn how to use the various features, check out the Documentation: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui/tree/main/docs Installation One-click installers | Windows | Linux | macOS | WSL ||--------|--------|--------|--------|| oobabooga-windows.zip | oobabooga-linux.zip | oobabooga-macos.zip | oobabooga-wsl.zip | Just download the zip above, extract it, and double-click on "start". The web UI and all its dependencies will be installed in the same folder. The source codes and more information can be found here: https://github.com/oobabooga/one-click-installers There is no need to run the installers as admin. Huge thanks to @jllllll , @ClayShoaf , and @xNul for their contributions to these installers. Manual installation using Conda Recommended if you have some experience with the command-line. 0. Install Conda https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html On Linux or WSL, it can be automatically installed with these two commands ( source ): curl -sL "https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh" > "Miniconda3.sh"bash Miniconda3.sh 1. Create a new conda environment conda create -n textgen python=3.10.9conda activate textgen 2. Install Pytorch | System | GPU | Command ||--------|---------|---------|| Linux/WSL | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Linux/WSL | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu || Linux | AMD | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm5.4.2 || MacOS + MPS | Any | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Windows | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu117 || Windows | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio | The up-to-date commands can be found here: https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/. 2.1 Additional information MacOS users: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui/pull/393 AMD users: https://rentry.org/eq3hg 3. Install the web UI git clone https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webuicd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt llama.cpp on AMD, Metal, and some specific CPUs Precompiled wheels are included for CPU-only and NVIDIA GPUs (cuBLAS). For AMD, Metal, and some specific CPUs, you need to uninstall those wheels and compile llama-cpp-python yourself. To uninstall: pip uninstall -y llama-cpp-python llama-cpp-python-cuda To compile: https://github.com/abetlen/llama-cpp-python#installation-with-openblas--cublas--clblast--metal bitsandbytes on older NVIDIA GPUs bitsandbytes >= 0.39 may not work. In that case, to use --load-in-8bit , you may have to downgrade like this: Linux: pip install bitsandbytes==0.38.1 Windows: pip install https://github.com/jllllll/bitsandbytes-windows-webui/raw/main/bitsandbytes-0.38.1-py3-none-any.whl Alternative: Docker ```ln -s docker/{Dockerfile,docker-compose.yml,.dockerignore} .cp docker/.env.example .env Edit .env and set TORCH CUDA ARCH_LIST based on your GPU model docker compose up --build``` You need to have docker compose v2.17 or higher installed. See this guide for instructions. For additional docker files, check out this repository . Updating the requirements From time to time, the requirements.txt changes. To update, use these commands: conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt --upgrade Downloading models Models should be placed in the text-generation-webui/models folder. They are usually downloaded from Hugging Face . Transformers or GPTQ models are made of several files and must be placed in a subfolder. Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── lmsys_vicuna-33b-v1.3│ │ ├── config.json│ │ ├── generation_config.json│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00001-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00002-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00003-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00004-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00005-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00006-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00007-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model.bin.index.json│ │ ├── special_tokens_map.json│ │ ├── tokenizer_config.json│ │ └── tokenizer.model In the "Model" tab of the UI, those models can be automatically downloaded from Hugging Face. You can also download them via the command-line with python download-model.py organization/model . GGML/GGUF models are a single file and should be placed directly into models . Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── llama-13b.ggmlv3.q4_K_M.bin Those models must be downloaded manually, as they are not currently supported by the automated downloader. GPT-4chan Instructions GPT-4chan has been shut down from Hugging Face, so you need to download it elsewhere. You have two options: Torrent: 16-bit / 32-bit Direct download: 16-bit / 32-bit The 32-bit version is only relevant if you intend to run the model in CPU mode. Otherwise, you should use the 16-bit version. After downloading the model, follow these steps: Place the files under models/gpt4chan_model_float16 or models/gpt4chan_model . Place GPT-J 6B's config.json file in that same folder: config.json . Download GPT-J 6B's tokenizer files (they will be automatically detected when you attempt to load GPT-4chan): python download-model.py EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B --text-only When you load this model in default or notebook modes, the "HTML" tab will show the generated text in 4chan format: Starting the web UI conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipython server.py Then browse to http://localhost:7860/?__theme=dark Optionally, you can use the following command-line flags: Basic settings | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| -h , --help | Show this help message and exit. || --multi-user | Multi-user mode. Chat histories are not saved or automatically loaded. WARNING: this is highly experimental. || --character CHARACTER | The name of the character to load in chat mode by default. || --model MODEL | Name of the model to load by default. || --lora LORA [LORA ...] | The list of LoRAs to load. If you want to load more than one LoRA, write the names separated by spaces. || --model-dir MODEL_DIR | Path to directory with all the models. || --lora-dir LORA_DIR | Path to directory with all the loras. || --model-menu | Show a model menu in the terminal when the web UI is first launched. || --settings SETTINGS_FILE | Load the default interface settings from this yaml file. See settings-template.yaml for an example. If you create a file called settings.yaml , this file will be loaded by default without the need to use the --settings flag. || --extensions EXTENSIONS [EXTENSIONS ...] | The list of extensions to load. If you want to load more than one extension, write the names separated by spaces. || --verbose | Print the prompts to the terminal. | Model loader | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| --loader LOADER | Choose the model loader manually, otherwise, it will get autodetected. Valid options: transformers, autogptq, gptq-for-llama, exllama, exllama_hf, llamacpp, rwkv, ctransformers | Accelerate/transformers | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --cpu | Use the CPU to generate text. Warning: Training on CPU is extremely slow.|| --auto-devices | Automatically split the model across the available GPU(s) and CPU. || --gpu-memory GPU_MEMORY [GPU_MEMORY ...] | Maximum GPU memory in GiB to be allocated per GPU. Example: --gpu-memory 10 for a single GPU, --gpu-memory 10 5 for two GPUs. You can also set values in MiB like --gpu-memory 3500MiB . || --cpu-memory CPU_MEMORY | Maximum CPU memory in GiB to allocate for offloaded weights. Same as above.|| --disk | If the model is too large for your GPU(s) and CPU combined, send the remaining layers to the disk. || --disk-cache-dir DISK_CACHE_DIR | Directory to save the disk cache to. Defaults to cache/ . || --load-in-8bit | Load the model with 8-bit precision (using bitsandbytes).|| --bf16 | Load the model with bfloat16 precision. Requires NVIDIA Ampere GPU. || --no-cache | Set use_cache to False while generating text. This reduces the VRAM usage a bit with a performance cost. || --xformers | Use xformer's memory efficient attention. This should increase your tokens/s. || --sdp-attention | Use torch 2.0's sdp attention. || --trust-remote-code | Set trust remote code=True while loading a model. Necessary for ChatGLM and Falcon. | Accelerate 4-bit ⚠️ Requires minimum compute of 7.0 on Windows at the moment. | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --load-in-4bit | Load the model with 4-bit precision (using bitsandbytes). || --compute_dtype COMPUTE_DTYPE | compute dtype for 4-bit. Valid options: bfloat16, float16, float32. || --quant_type QUANT_TYPE | quant type for 4-bit. Valid options: nf4, fp4. || --use_double_quant | use double_quant for 4-bit. | GGML/GGUF (for llama.cpp and ctransformers) | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --threads | Number of threads to use. || --n_batch | Maximum number of prompt tokens to batch together when calling llama_eval. || --n-gpu-layers N_GPU_LAYERS | Number of layers to offload to the GPU. Only works if llama-cpp-python was compiled with BLAS. Set this to 1000000000 to offload all layers to the GPU. || --n_ctx N_CTX | Size of the prompt context. | llama.cpp | Flag | Description ||---------------|---------------|| --no-mmap | Prevent mmap from being used. || --mlock | Force the system to keep the model in RAM. || --mul_mat_q | Activate new mulmat kernels. || --cache-capacity CACHE_CAPACITY | Maximum cache capacity. Examples: 2000MiB, 2GiB. When provided without units, bytes will be assumed. || --tensor_split TENSOR_SPLIT | Split the model across multiple GPUs, comma-separated list of proportions, e.g. 18,17 || --llama_cpp_seed SEED | Seed for llama-cpp models. Default 0 (random). || --n_gqa N_GQA | GGML only (not used by GGUF): Grouped-Query Attention. Must be 8 for llama-2 70b. || --rms_norm_eps RMS_NORM_EPS | GGML only (not used by GGUF): 5e-6 is a good value for llama-2 models. || --cpu | Use the CPU version of llama-cpp-python instead of the GPU-accelerated version. || --cfg-cache | llamacpp_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. | ctransformers | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently gpt2, gptj, gptneox, falcon, llama, mpt, starcoder (gptbigcode), dollyv2, and replit are supported. | AutoGPTQ | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --triton | Use triton. || --no_inject_fused_attention | Disable the use of fused attention, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_inject_fused_mlp | Triton mode only: disable the use of fused MLP, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_use_cuda_fp16 | This can make models faster on some systems. || --desc_act | For models that don't have a quantize config.json, this parameter is used to define whether to set desc act or not in BaseQuantizeConfig. || --disable_exllama | Disable ExLlama kernel, which can improve inference speed on some systems. | ExLlama | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --gpu-split | Comma-separated list of VRAM (in GB) to use per GPU device for model layers, e.g. 20,7,7 || --max_seq_len MAX_SEQ_LEN | Maximum sequence length. || --cfg-cache | ExLlama_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. Necessary to use CFG with that loader, but not necessary for CFG with base ExLlama. | GPTQ-for-LLaMa | Flag | Description ||---------------------------|-------------|| --wbits WBITS | Load a pre-quantized model with specified precision in bits. 2, 3, 4 and 8 are supported. || --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently LLaMA, OPT, and GPT-J are supported. || --groupsize GROUPSIZE | Group size. || --pre_layer PRE_LAYER [PRE_LAYER ...] | The number of layers to allocate to the GPU. Setting this parameter enables CPU offloading for 4-bit models. For multi-gpu, write the numbers separated by spaces, eg --pre_layer 30 60 . || --checkpoint CHECKPOINT | The path to the quantized checkpoint file. If not specified, it will be automatically detected. || --monkey-patch | Apply the monkey patch for using LoRAs with quantized models. DeepSpeed | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --deepspeed | Enable the use of DeepSpeed ZeRO-3 for inference via the Transformers integration. || --nvme-offload-dir NVME_OFFLOAD_DIR | DeepSpeed: Directory to use for ZeRO-3 NVME offloading. || --local_rank LOCAL_RANK | DeepSpeed: Optional argument for distributed setups. | RWKV | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------|-------------|| --rwkv-strategy RWKV_STRATEGY | RWKV: The strategy to use while loading the model. Examples: "cpu fp32", "cuda fp16", "cuda fp16i8". || --rwkv-cuda-on | RWKV: Compile the CUDA kernel for better performance. | RoPE (for llama.cpp, ExLlama, and transformers) | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --alpha_value ALPHA_VALUE | Positional embeddings alpha factor for NTK RoPE scaling. Use either this or compress pos emb, not both. || --rope_freq_base ROPE_FREQ_BASE | If greater than 0, will be used instead of alpha value. Those two are related by rope freq base = 10000 * alpha value ^ (64 / 63). || --compress_pos_emb COMPRESS_POS_EMB | Positional embeddings compression factor. Should be set to (context length) / (model's original context length). Equal to 1/rope freq scale. | Gradio | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --listen | Make the web UI reachable from your local network. || --listen-host LISTEN_HOST | The hostname that the server will use. || --listen-port LISTEN_PORT | The listening port that the server will use. || --share | Create a public URL. This is useful for running the web UI on Google Colab or similar. || --auto-launch | Open the web UI in the default browser upon launch. || --gradio-auth USER:PWD | set gradio authentication like "username:password"; or comma-delimit multiple like "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --gradio-auth-path GRADIO_AUTH_PATH | Set the gradio authentication file path. The file should contain one or more user:password pairs in this format: "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --ssl-keyfile SSL_KEYFILE | The path to the SSL certificate key file. || --ssl-certfile SSL_CERTFILE | The path to the SSL certificate cert file. | API | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --api | Enable the API extension. || --public-api | Create a public URL for the API using Cloudfare. || --public-api-id PUBLIC_API_ID | Tunnel ID for named Cloudflare Tunnel. Use together with public-api option. || --api-blocking-port BLOCKING_PORT | The listening port for the blocking API. || --api-streaming-port STREAMING_PORT | The listening port for the streaming API. | Multimodal | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --multimodal-pipeline PIPELINE | The multimodal pipeline to use. Examples: llava-7b , llava-13b . | Presets Inference settings presets can be created under presets/ as yaml files. These files are detected automatically at startup. The presets that are included by default are the result of a contest that received 7215 votes. More details can be found here . Contributing If you would like to contribute to the project, check out the Contributing guidelines . Community Subreddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/oobabooga/ Discord: https://discord.gg/jwZCF2dPQN Acknowledgment In August 2023, Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) provided a generous grant to encourage and support my independent work on this project. I am extremely grateful for their trust and recognition, which will allow me to dedicate more time towards realizing the full potential of text-generation-webui. To restore the repository download the bundle wget https://archive.org/download/github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-27_06-13-21/oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-27_06-13-21.bundle and run: git clone oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-27_06-13-21.bundle Source: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui Uploader: oobabooga Upload date: 2023-08-27
“Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-27_06-13-21” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-27_06-13-21
- Author: oobabooga
“Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-27_06-13-21” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ➤ github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-27_06-13-21
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "software" format, the size of the file-s is: 3.96 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 63 times, the file-s went public at Sun Aug 27 2023.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - JPEG - JPEG Thumb - Metadata - Unknown -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-27_06-13-21 at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
3DTIC ADA183796: The Lexicon In Text Generation.
By Defense Technical Information Center
This report compares several lexicons used in computational text generation systems, with respects to the size of the lexical item, the way occurrence phenomena are represented, and the way semantic information is included. The lexicons examined can be roughly divided into two principal groups with respect to the size of the item, phrasal lexicons and word-based lexicons. Phrasal lexicons, which are more numerous, have large units (sometimes whole sentences) stored as lexical entries. They often tend to represent syntactic structure within the lexical item, and may also contain variables or slots which can be filled by other items. This type of lexicon generally provides the primary line between semantic and syntactic representation by mapping semantic structures onto syntactic structures. The word-based lexicon, on the otherhand, merely inserts words into previously built syntactic structures, using feature specifications to guide the process. Lexicons also vary with respect to the amount of occurrence information they contain. Most lexicons represent subcate; organizational (argument structure) information, either by means of features or with syntactically labelled slots. They can also have noncompositional multi-word units (idioms) as lexical entries. Some lexicons represent selectional information as well, by means of semantic feature restriction on slots. collocational information is rarely included. The meaning of a lexical item can be indicated by a pointer to a concept in a semantic network or by a pattern which matches a piece of conceptual structure. Some systems additionally have a concept of lexical choice, i.e., routines which explicitly choose between alternative lexical realizations of a particular meaning.
“DTIC ADA183796: The Lexicon In Text Generation.” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA183796: The Lexicon In Text Generation.
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA183796: The Lexicon In Text Generation.” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Cumming,Susanna - UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA MARINA DEL REY INFORMATION SCIENCES INST - *VOCABULARY - *TEXT PROCESSING - LABELED SUBSTANCES - LEXICOGRAPHY - MAPPING - SEMANTICS - SLOTS - STRUCTURES - SYNTAX - VOCABULARY - WORDS(LANGUAGE) - TABLES(DATA) - COMPUTER FILES - NATURAL LANGUAGE
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA183796
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 31.69 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 76 times, the file-s went public at Thu Feb 15 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA183796: The Lexicon In Text Generation. at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
4DTIC ADA134491: A Linguistic Overview Of The Nigel Text Generation Grammar.
By Defense Technical Information Center
Recent text generation research resembles recent research in synthesis of vaccines. The research is designed to construct entities which previously arose naturally. This constructive approach creates practical and theoretical benefits. Our text generation research has produced a large systemic English grammar, which is embedded in a computer program. This grammar, which is called Nigel, generates sentences. It is controlled by a semantic stratum which has been added to the basic systemic framework. This paper describes the program, which also is called Nigel. It identifies augmentations of various precedents in the systemic framework, and it indicates the current status of the program. The paper has a dual focus. First, on Nigel's processes, it describes the methods Nigel uses to control text to fulfill a purpose by using its new semantic stratum. Second, concerning Nigel's interactions with its environment, it shows reasons why Nigel is easily embedded in a larger experimental program. Although the paper does not focus on Nigel's syntactic scope, that its scope is non-trivial is indicated by the fact that all of the sentence and clause structures of this abstract are within that syntactic scope. (Author)
“DTIC ADA134491: A Linguistic Overview Of The Nigel Text Generation Grammar.” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA134491: A Linguistic Overview Of The Nigel Text Generation Grammar.
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA134491: A Linguistic Overview Of The Nigel Text Generation Grammar.” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Mann,William C - UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA MARINA DEL REY INFORMATION SCIENCES INST - *Text processing - *Artificial intelligence - Grammars - Computer programs - Natural language - English language - Algorithms - Semantics - Syntax
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA134491
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 10.50 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 93 times, the file-s went public at Mon Jan 15 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA134491: A Linguistic Overview Of The Nigel Text Generation Grammar. at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
5DTIC ADA269670: Automatic Documentation Generation: The Interaction Of Text And Examples
By Defense Technical Information Center
Good documentation is critical for user acceptance of any system, and empirical studies have shown that examples can greatly increase effectiveness of system documentation. However, studies also show that badly integrated text and examples can be actually detrimental compared to using either text or examples alone. It is thus clear that in order to provide useful documentation automatically, a system must be capable of providing well-integrated examples to illustrate its points. Precious work on example generation has concentrated on the issue of retrieving or constructing examples. In this paper, we look at the integration of text and examples. We identify how text and examples co-constrain each other and show that a system must consider example generation as an integral part of the generation process. Finally, we present such a system, together with example. Documentation, Natural language generation examples.
“DTIC ADA269670: Automatic Documentation Generation: The Interaction Of Text And Examples” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA269670: Automatic Documentation Generation: The Interaction Of Text And Examples
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA269670: Automatic Documentation Generation: The Interaction Of Text And Examples” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Mittal, Vibhu O - UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA MARINA DEL REY INFORMATION SCIENCES INST - *INTERACTIONS - *TEXT PROCESSING - ACCEPTANCE TESTS - INTEGRALS - INTEGRATION - USER NEEDS - KNOWLEDGE BASED SYSTEMS - NATURAL LANGUAGE
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA269670
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 12.19 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 52 times, the file-s went public at Mon Mar 12 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA269670: Automatic Documentation Generation: The Interaction Of Text And Examples at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
6Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30
By oobabooga
A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Supports transformers, GPTQ, llama.cpp (ggml/gguf), Llama models. Text generation web UI A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Its goal is to become the AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui of text generation. | | ||:---:|:---:|| | | Features 3 interface modes: default (two columns), notebook, and chat Multiple model backends: transformers , llama.cpp , ExLlama , AutoGPTQ , GPTQ-for-LLaMa , ctransformers Dropdown menu for quickly switching between different models LoRA: load and unload LoRAs on the fly, train a new LoRA using QLoRA Precise instruction templates for chat mode, including Llama-2-chat, Alpaca, Vicuna, WizardLM, StableLM, and many others 4-bit, 8-bit, and CPU inference through the transformers library Use llama.cpp models with transformers samplers ( llamacpp_HF loader) Multimodal pipelines, including LLaVA and MiniGPT-4 Extensions framework Custom chat characters Very efficient text streaming Markdown output with LaTeX rendering, to use for instance with GALACTICA API, including endpoints for websocket streaming ( see the examples ) To learn how to use the various features, check out the Documentation: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui/tree/main/docs Installation One-click installers | Windows | Linux | macOS | WSL ||--------|--------|--------|--------|| oobabooga-windows.zip | oobabooga-linux.zip | oobabooga-macos.zip | oobabooga-wsl.zip | Just download the zip above, extract it, and double-click on "start". The web UI and all its dependencies will be installed in the same folder. The source codes and more information can be found here: https://github.com/oobabooga/one-click-installers There is no need to run the installers as admin. Huge thanks to @jllllll , @ClayShoaf , and @xNul for their contributions to these installers. Manual installation using Conda Recommended if you have some experience with the command-line. 0. Install Conda https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html On Linux or WSL, it can be automatically installed with these two commands ( source ): curl -sL "https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh" > "Miniconda3.sh"bash Miniconda3.sh 1. Create a new conda environment conda create -n textgen python=3.10.9conda activate textgen 2. Install Pytorch | System | GPU | Command ||--------|---------|---------|| Linux/WSL | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Linux/WSL | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu || Linux | AMD | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm5.4.2 || MacOS + MPS | Any | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Windows | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu117 || Windows | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio | The up-to-date commands can be found here: https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/. 3. Install the web UI git clone https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webuicd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt AMD, Metal, Intel Arc, and CPUs without AVCX2 1) Replace the last command above with pip install -r requirements_nocuda.txt 2) Manually install llama-cpp-python using the appropriate command for your hardware: Installation from PyPI . 3) AMD: Manually install AutoGPTQ: Installation . 4) AMD: Manually install ExLlama by simply cloning it into the repositories folder (it will be automatically compiled at runtime after that): cd text-generation-webuimkdir repositoriescd repositoriesgit clone https://github.com/turboderp/exllama bitsandbytes on older NVIDIA GPUs bitsandbytes >= 0.39 may not work. In that case, to use --load-in-8bit , you may have to downgrade like this: Linux: pip install bitsandbytes==0.38.1 Windows: pip install https://github.com/jllllll/bitsandbytes-windows-webui/raw/main/bitsandbytes-0.38.1-py3-none-any.whl Alternative: Docker ```ln -s docker/{Dockerfile,docker-compose.yml,.dockerignore} .cp docker/.env.example .env Edit .env and set TORCH CUDA ARCH_LIST based on your GPU model docker compose up --build``` You need to have docker compose v2.17 or higher installed. See this guide for instructions. For additional docker files, check out this repository . Updating the requirements From time to time, the requirements.txt changes. To update, use these commands: conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt --upgrade Downloading models Models should be placed in the text-generation-webui/models folder. They are usually downloaded from Hugging Face . Transformers or GPTQ models are made of several files and must be placed in a subfolder. Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── lmsys_vicuna-33b-v1.3│ │ ├── config.json│ │ ├── generation_config.json│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00001-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00002-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00003-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00004-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00005-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00006-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00007-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model.bin.index.json│ │ ├── special_tokens_map.json│ │ ├── tokenizer_config.json│ │ └── tokenizer.model GGML/GGUF models are a single file and should be placed directly into models . Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── llama-13b.ggmlv3.q4_K_M.bin In both cases, you can use the "Model" tab of the UI to download the model from Hugging Face automatically. It is also possible to download via the command-line with python download-model.py organization/model (use --help to see all the options). GPT-4chan Instructions GPT-4chan has been shut down from Hugging Face, so you need to download it elsewhere. You have two options: Torrent: 16-bit / 32-bit Direct download: 16-bit / 32-bit The 32-bit version is only relevant if you intend to run the model in CPU mode. Otherwise, you should use the 16-bit version. After downloading the model, follow these steps: Place the files under models/gpt4chan_model_float16 or models/gpt4chan_model . Place GPT-J 6B's config.json file in that same folder: config.json . Download GPT-J 6B's tokenizer files (they will be automatically detected when you attempt to load GPT-4chan): python download-model.py EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B --text-only When you load this model in default or notebook modes, the "HTML" tab will show the generated text in 4chan format: Starting the web UI conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipython server.py Then browse to http://localhost:7860/?__theme=dark Optionally, you can use the following command-line flags: Basic settings | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| -h , --help | Show this help message and exit. || --multi-user | Multi-user mode. Chat histories are not saved or automatically loaded. WARNING: this is highly experimental. || --character CHARACTER | The name of the character to load in chat mode by default. || --model MODEL | Name of the model to load by default. || --lora LORA [LORA ...] | The list of LoRAs to load. If you want to load more than one LoRA, write the names separated by spaces. || --model-dir MODEL_DIR | Path to directory with all the models. || --lora-dir LORA_DIR | Path to directory with all the loras. || --model-menu | Show a model menu in the terminal when the web UI is first launched. || --settings SETTINGS_FILE | Load the default interface settings from this yaml file. See settings-template.yaml for an example. If you create a file called settings.yaml , this file will be loaded by default without the need to use the --settings flag. || --extensions EXTENSIONS [EXTENSIONS ...] | The list of extensions to load. If you want to load more than one extension, write the names separated by spaces. || --verbose | Print the prompts to the terminal. | Model loader | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| --loader LOADER | Choose the model loader manually, otherwise, it will get autodetected. Valid options: transformers, autogptq, gptq-for-llama, exllama, exllama_hf, llamacpp, rwkv, ctransformers | Accelerate/transformers | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --cpu | Use the CPU to generate text. Warning: Training on CPU is extremely slow.|| --auto-devices | Automatically split the model across the available GPU(s) and CPU. || --gpu-memory GPU_MEMORY [GPU_MEMORY ...] | Maximum GPU memory in GiB to be allocated per GPU. Example: --gpu-memory 10 for a single GPU, --gpu-memory 10 5 for two GPUs. You can also set values in MiB like --gpu-memory 3500MiB . || --cpu-memory CPU_MEMORY | Maximum CPU memory in GiB to allocate for offloaded weights. Same as above.|| --disk | If the model is too large for your GPU(s) and CPU combined, send the remaining layers to the disk. || --disk-cache-dir DISK_CACHE_DIR | Directory to save the disk cache to. Defaults to cache/ . || --load-in-8bit | Load the model with 8-bit precision (using bitsandbytes).|| --bf16 | Load the model with bfloat16 precision. Requires NVIDIA Ampere GPU. || --no-cache | Set use_cache to False while generating text. This reduces the VRAM usage a bit with a performance cost. || --xformers | Use xformer's memory efficient attention. This should increase your tokens/s. || --sdp-attention | Use torch 2.0's sdp attention. || --trust-remote-code | Set trust remote code=True while loading a model. Necessary for ChatGLM and Falcon. | Accelerate 4-bit ⚠️ Requires minimum compute of 7.0 on Windows at the moment. | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --load-in-4bit | Load the model with 4-bit precision (using bitsandbytes). || --compute_dtype COMPUTE_DTYPE | compute dtype for 4-bit. Valid options: bfloat16, float16, float32. || --quant_type QUANT_TYPE | quant type for 4-bit. Valid options: nf4, fp4. || --use_double_quant | use double_quant for 4-bit. | GGML/GGUF (for llama.cpp and ctransformers) | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --threads | Number of threads to use. || --n_batch | Maximum number of prompt tokens to batch together when calling llama_eval. || --n-gpu-layers N_GPU_LAYERS | Number of layers to offload to the GPU. Only works if llama-cpp-python was compiled with BLAS. Set this to 1000000000 to offload all layers to the GPU. || --n_ctx N_CTX | Size of the prompt context. | llama.cpp | Flag | Description ||---------------|---------------|| --no-mmap | Prevent mmap from being used. || --mlock | Force the system to keep the model in RAM. || --mul_mat_q | Activate new mulmat kernels. || --cache-capacity CACHE_CAPACITY | Maximum cache capacity. Examples: 2000MiB, 2GiB. When provided without units, bytes will be assumed. || --tensor_split TENSOR_SPLIT | Split the model across multiple GPUs, comma-separated list of proportions, e.g. 18,17 || --llama_cpp_seed SEED | Seed for llama-cpp models. Default 0 (random). || --n_gqa N_GQA | GGML only (not used by GGUF): Grouped-Query Attention. Must be 8 for llama-2 70b. || --rms_norm_eps RMS_NORM_EPS | GGML only (not used by GGUF): 5e-6 is a good value for llama-2 models. || --cpu | Use the CPU version of llama-cpp-python instead of the GPU-accelerated version. || --cfg-cache | llamacpp_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. | ctransformers | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently gpt2, gptj, gptneox, falcon, llama, mpt, starcoder (gptbigcode), dollyv2, and replit are supported. | AutoGPTQ | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --triton | Use triton. || --no_inject_fused_attention | Disable the use of fused attention, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_inject_fused_mlp | Triton mode only: disable the use of fused MLP, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_use_cuda_fp16 | This can make models faster on some systems. || --desc_act | For models that don't have a quantize config.json, this parameter is used to define whether to set desc act or not in BaseQuantizeConfig. || --disable_exllama | Disable ExLlama kernel, which can improve inference speed on some systems. | ExLlama | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --gpu-split | Comma-separated list of VRAM (in GB) to use per GPU device for model layers, e.g. 20,7,7 || --max_seq_len MAX_SEQ_LEN | Maximum sequence length. || --cfg-cache | ExLlama_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. Necessary to use CFG with that loader, but not necessary for CFG with base ExLlama. | GPTQ-for-LLaMa | Flag | Description ||---------------------------|-------------|| --wbits WBITS | Load a pre-quantized model with specified precision in bits. 2, 3, 4 and 8 are supported. || --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently LLaMA, OPT, and GPT-J are supported. || --groupsize GROUPSIZE | Group size. || --pre_layer PRE_LAYER [PRE_LAYER ...] | The number of layers to allocate to the GPU. Setting this parameter enables CPU offloading for 4-bit models. For multi-gpu, write the numbers separated by spaces, eg --pre_layer 30 60 . || --checkpoint CHECKPOINT | The path to the quantized checkpoint file. If not specified, it will be automatically detected. || --monkey-patch | Apply the monkey patch for using LoRAs with quantized models. DeepSpeed | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --deepspeed | Enable the use of DeepSpeed ZeRO-3 for inference via the Transformers integration. || --nvme-offload-dir NVME_OFFLOAD_DIR | DeepSpeed: Directory to use for ZeRO-3 NVME offloading. || --local_rank LOCAL_RANK | DeepSpeed: Optional argument for distributed setups. | RWKV | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------|-------------|| --rwkv-strategy RWKV_STRATEGY | RWKV: The strategy to use while loading the model. Examples: "cpu fp32", "cuda fp16", "cuda fp16i8". || --rwkv-cuda-on | RWKV: Compile the CUDA kernel for better performance. | RoPE (for llama.cpp, ExLlama, and transformers) | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --alpha_value ALPHA_VALUE | Positional embeddings alpha factor for NTK RoPE scaling. Use either this or compress pos emb, not both. || --rope_freq_base ROPE_FREQ_BASE | If greater than 0, will be used instead of alpha value. Those two are related by rope freq base = 10000 * alpha value ^ (64 / 63). || --compress_pos_emb COMPRESS_POS_EMB | Positional embeddings compression factor. Should be set to (context length) / (model's original context length). Equal to 1/rope freq scale. | Gradio | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --listen | Make the web UI reachable from your local network. || --listen-host LISTEN_HOST | The hostname that the server will use. || --listen-port LISTEN_PORT | The listening port that the server will use. || --share | Create a public URL. This is useful for running the web UI on Google Colab or similar. || --auto-launch | Open the web UI in the default browser upon launch. || --gradio-auth USER:PWD | set gradio authentication like "username:password"; or comma-delimit multiple like "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --gradio-auth-path GRADIO_AUTH_PATH | Set the gradio authentication file path. The file should contain one or more user:password pairs in this format: "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --ssl-keyfile SSL_KEYFILE | The path to the SSL certificate key file. || --ssl-certfile SSL_CERTFILE | The path to the SSL certificate cert file. | API | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --api | Enable the API extension. || --public-api | Create a public URL for the API using Cloudfare. || --public-api-id PUBLIC_API_ID | Tunnel ID for named Cloudflare Tunnel. Use together with public-api option. || --api-blocking-port BLOCKING_PORT | The listening port for the blocking API. || --api-streaming-port STREAMING_PORT | The listening port for the streaming API. | Multimodal | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --multimodal-pipeline PIPELINE | The multimodal pipeline to use. Examples: llava-7b , llava-13b . | Presets Inference settings presets can be created under presets/ as yaml files. These files are detected automatically at startup. The presets that are included by default are the result of a contest that received 7215 votes. More details can be found here . Contributing If you would like to contribute to the project, check out the Contributing guidelines . Community Subreddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/oobabooga/ Discord: https://discord.gg/jwZCF2dPQN Acknowledgment In August 2023, Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) provided a generous grant to encourage and support my independent work on this project. I am extremely grateful for their trust and recognition, which will allow me to dedicate more time towards realizing the full potential of text-generation-webui. To restore the repository download the bundle wget https://archive.org/download/github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30/oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30.bundle and run: git clone oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30.bundle Source: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui Uploader: oobabooga Upload date: 2023-08-30
“Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30
- Author: oobabooga
“Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ➤ github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "software" format, the size of the file-s is: 3.93 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 38 times, the file-s went public at Thu Aug 31 2023.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - JPEG - JPEG Thumb - Metadata - Unknown -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30 at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
7Computational Text Generation : Generation From Data Or Linguistic Structure, Text Planning - Sentence Generation, Explanation Generation : Bibliography
By Sabourin, Conrad, 1943-
A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Supports transformers, GPTQ, llama.cpp (ggml/gguf), Llama models. Text generation web UI A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Its goal is to become the AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui of text generation. | | ||:---:|:---:|| | | Features 3 interface modes: default (two columns), notebook, and chat Multiple model backends: transformers , llama.cpp , ExLlama , AutoGPTQ , GPTQ-for-LLaMa , ctransformers Dropdown menu for quickly switching between different models LoRA: load and unload LoRAs on the fly, train a new LoRA using QLoRA Precise instruction templates for chat mode, including Llama-2-chat, Alpaca, Vicuna, WizardLM, StableLM, and many others 4-bit, 8-bit, and CPU inference through the transformers library Use llama.cpp models with transformers samplers ( llamacpp_HF loader) Multimodal pipelines, including LLaVA and MiniGPT-4 Extensions framework Custom chat characters Very efficient text streaming Markdown output with LaTeX rendering, to use for instance with GALACTICA API, including endpoints for websocket streaming ( see the examples ) To learn how to use the various features, check out the Documentation: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui/tree/main/docs Installation One-click installers | Windows | Linux | macOS | WSL ||--------|--------|--------|--------|| oobabooga-windows.zip | oobabooga-linux.zip | oobabooga-macos.zip | oobabooga-wsl.zip | Just download the zip above, extract it, and double-click on "start". The web UI and all its dependencies will be installed in the same folder. The source codes and more information can be found here: https://github.com/oobabooga/one-click-installers There is no need to run the installers as admin. Huge thanks to @jllllll , @ClayShoaf , and @xNul for their contributions to these installers. Manual installation using Conda Recommended if you have some experience with the command-line. 0. Install Conda https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html On Linux or WSL, it can be automatically installed with these two commands ( source ): curl -sL "https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh" > "Miniconda3.sh"bash Miniconda3.sh 1. Create a new conda environment conda create -n textgen python=3.10.9conda activate textgen 2. Install Pytorch | System | GPU | Command ||--------|---------|---------|| Linux/WSL | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Linux/WSL | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu || Linux | AMD | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm5.4.2 || MacOS + MPS | Any | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Windows | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu117 || Windows | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio | The up-to-date commands can be found here: https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/. 3. Install the web UI git clone https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webuicd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt AMD, Metal, Intel Arc, and CPUs without AVCX2 1) Replace the last command above with pip install -r requirements_nocuda.txt 2) Manually install llama-cpp-python using the appropriate command for your hardware: Installation from PyPI . 3) AMD: Manually install AutoGPTQ: Installation . 4) AMD: Manually install ExLlama by simply cloning it into the repositories folder (it will be automatically compiled at runtime after that): cd text-generation-webuimkdir repositoriescd repositoriesgit clone https://github.com/turboderp/exllama bitsandbytes on older NVIDIA GPUs bitsandbytes >= 0.39 may not work. In that case, to use --load-in-8bit , you may have to downgrade like this: Linux: pip install bitsandbytes==0.38.1 Windows: pip install https://github.com/jllllll/bitsandbytes-windows-webui/raw/main/bitsandbytes-0.38.1-py3-none-any.whl Alternative: Docker ```ln -s docker/{Dockerfile,docker-compose.yml,.dockerignore} .cp docker/.env.example .env Edit .env and set TORCH CUDA ARCH_LIST based on your GPU model docker compose up --build``` You need to have docker compose v2.17 or higher installed. See this guide for instructions. For additional docker files, check out this repository . Updating the requirements From time to time, the requirements.txt changes. To update, use these commands: conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt --upgrade Downloading models Models should be placed in the text-generation-webui/models folder. They are usually downloaded from Hugging Face . Transformers or GPTQ models are made of several files and must be placed in a subfolder. Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── lmsys_vicuna-33b-v1.3│ │ ├── config.json│ │ ├── generation_config.json│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00001-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00002-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00003-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00004-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00005-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00006-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00007-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model.bin.index.json│ │ ├── special_tokens_map.json│ │ ├── tokenizer_config.json│ │ └── tokenizer.model GGML/GGUF models are a single file and should be placed directly into models . Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── llama-13b.ggmlv3.q4_K_M.bin In both cases, you can use the "Model" tab of the UI to download the model from Hugging Face automatically. It is also possible to download via the command-line with python download-model.py organization/model (use --help to see all the options). GPT-4chan Instructions GPT-4chan has been shut down from Hugging Face, so you need to download it elsewhere. You have two options: Torrent: 16-bit / 32-bit Direct download: 16-bit / 32-bit The 32-bit version is only relevant if you intend to run the model in CPU mode. Otherwise, you should use the 16-bit version. After downloading the model, follow these steps: Place the files under models/gpt4chan_model_float16 or models/gpt4chan_model . Place GPT-J 6B's config.json file in that same folder: config.json . Download GPT-J 6B's tokenizer files (they will be automatically detected when you attempt to load GPT-4chan): python download-model.py EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B --text-only When you load this model in default or notebook modes, the "HTML" tab will show the generated text in 4chan format: Starting the web UI conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipython server.py Then browse to http://localhost:7860/?__theme=dark Optionally, you can use the following command-line flags: Basic settings | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| -h , --help | Show this help message and exit. || --multi-user | Multi-user mode. Chat histories are not saved or automatically loaded. WARNING: this is highly experimental. || --character CHARACTER | The name of the character to load in chat mode by default. || --model MODEL | Name of the model to load by default. || --lora LORA [LORA ...] | The list of LoRAs to load. If you want to load more than one LoRA, write the names separated by spaces. || --model-dir MODEL_DIR | Path to directory with all the models. || --lora-dir LORA_DIR | Path to directory with all the loras. || --model-menu | Show a model menu in the terminal when the web UI is first launched. || --settings SETTINGS_FILE | Load the default interface settings from this yaml file. See settings-template.yaml for an example. If you create a file called settings.yaml , this file will be loaded by default without the need to use the --settings flag. || --extensions EXTENSIONS [EXTENSIONS ...] | The list of extensions to load. If you want to load more than one extension, write the names separated by spaces. || --verbose | Print the prompts to the terminal. | Model loader | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| --loader LOADER | Choose the model loader manually, otherwise, it will get autodetected. Valid options: transformers, autogptq, gptq-for-llama, exllama, exllama_hf, llamacpp, rwkv, ctransformers | Accelerate/transformers | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --cpu | Use the CPU to generate text. Warning: Training on CPU is extremely slow.|| --auto-devices | Automatically split the model across the available GPU(s) and CPU. || --gpu-memory GPU_MEMORY [GPU_MEMORY ...] | Maximum GPU memory in GiB to be allocated per GPU. Example: --gpu-memory 10 for a single GPU, --gpu-memory 10 5 for two GPUs. You can also set values in MiB like --gpu-memory 3500MiB . || --cpu-memory CPU_MEMORY | Maximum CPU memory in GiB to allocate for offloaded weights. Same as above.|| --disk | If the model is too large for your GPU(s) and CPU combined, send the remaining layers to the disk. || --disk-cache-dir DISK_CACHE_DIR | Directory to save the disk cache to. Defaults to cache/ . || --load-in-8bit | Load the model with 8-bit precision (using bitsandbytes).|| --bf16 | Load the model with bfloat16 precision. Requires NVIDIA Ampere GPU. || --no-cache | Set use_cache to False while generating text. This reduces the VRAM usage a bit with a performance cost. || --xformers | Use xformer's memory efficient attention. This should increase your tokens/s. || --sdp-attention | Use torch 2.0's sdp attention. || --trust-remote-code | Set trust remote code=True while loading a model. Necessary for ChatGLM and Falcon. | Accelerate 4-bit ⚠️ Requires minimum compute of 7.0 on Windows at the moment. | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --load-in-4bit | Load the model with 4-bit precision (using bitsandbytes). || --compute_dtype COMPUTE_DTYPE | compute dtype for 4-bit. Valid options: bfloat16, float16, float32. || --quant_type QUANT_TYPE | quant type for 4-bit. Valid options: nf4, fp4. || --use_double_quant | use double_quant for 4-bit. | GGML/GGUF (for llama.cpp and ctransformers) | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --threads | Number of threads to use. || --n_batch | Maximum number of prompt tokens to batch together when calling llama_eval. || --n-gpu-layers N_GPU_LAYERS | Number of layers to offload to the GPU. Only works if llama-cpp-python was compiled with BLAS. Set this to 1000000000 to offload all layers to the GPU. || --n_ctx N_CTX | Size of the prompt context. | llama.cpp | Flag | Description ||---------------|---------------|| --no-mmap | Prevent mmap from being used. || --mlock | Force the system to keep the model in RAM. || --mul_mat_q | Activate new mulmat kernels. || --cache-capacity CACHE_CAPACITY | Maximum cache capacity. Examples: 2000MiB, 2GiB. When provided without units, bytes will be assumed. || --tensor_split TENSOR_SPLIT | Split the model across multiple GPUs, comma-separated list of proportions, e.g. 18,17 || --llama_cpp_seed SEED | Seed for llama-cpp models. Default 0 (random). || --n_gqa N_GQA | GGML only (not used by GGUF): Grouped-Query Attention. Must be 8 for llama-2 70b. || --rms_norm_eps RMS_NORM_EPS | GGML only (not used by GGUF): 5e-6 is a good value for llama-2 models. || --cpu | Use the CPU version of llama-cpp-python instead of the GPU-accelerated version. || --cfg-cache | llamacpp_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. | ctransformers | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently gpt2, gptj, gptneox, falcon, llama, mpt, starcoder (gptbigcode), dollyv2, and replit are supported. | AutoGPTQ | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --triton | Use triton. || --no_inject_fused_attention | Disable the use of fused attention, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_inject_fused_mlp | Triton mode only: disable the use of fused MLP, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_use_cuda_fp16 | This can make models faster on some systems. || --desc_act | For models that don't have a quantize config.json, this parameter is used to define whether to set desc act or not in BaseQuantizeConfig. || --disable_exllama | Disable ExLlama kernel, which can improve inference speed on some systems. | ExLlama | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --gpu-split | Comma-separated list of VRAM (in GB) to use per GPU device for model layers, e.g. 20,7,7 || --max_seq_len MAX_SEQ_LEN | Maximum sequence length. || --cfg-cache | ExLlama_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. Necessary to use CFG with that loader, but not necessary for CFG with base ExLlama. | GPTQ-for-LLaMa | Flag | Description ||---------------------------|-------------|| --wbits WBITS | Load a pre-quantized model with specified precision in bits. 2, 3, 4 and 8 are supported. || --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently LLaMA, OPT, and GPT-J are supported. || --groupsize GROUPSIZE | Group size. || --pre_layer PRE_LAYER [PRE_LAYER ...] | The number of layers to allocate to the GPU. Setting this parameter enables CPU offloading for 4-bit models. For multi-gpu, write the numbers separated by spaces, eg --pre_layer 30 60 . || --checkpoint CHECKPOINT | The path to the quantized checkpoint file. If not specified, it will be automatically detected. || --monkey-patch | Apply the monkey patch for using LoRAs with quantized models. DeepSpeed | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --deepspeed | Enable the use of DeepSpeed ZeRO-3 for inference via the Transformers integration. || --nvme-offload-dir NVME_OFFLOAD_DIR | DeepSpeed: Directory to use for ZeRO-3 NVME offloading. || --local_rank LOCAL_RANK | DeepSpeed: Optional argument for distributed setups. | RWKV | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------|-------------|| --rwkv-strategy RWKV_STRATEGY | RWKV: The strategy to use while loading the model. Examples: "cpu fp32", "cuda fp16", "cuda fp16i8". || --rwkv-cuda-on | RWKV: Compile the CUDA kernel for better performance. | RoPE (for llama.cpp, ExLlama, and transformers) | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --alpha_value ALPHA_VALUE | Positional embeddings alpha factor for NTK RoPE scaling. Use either this or compress pos emb, not both. || --rope_freq_base ROPE_FREQ_BASE | If greater than 0, will be used instead of alpha value. Those two are related by rope freq base = 10000 * alpha value ^ (64 / 63). || --compress_pos_emb COMPRESS_POS_EMB | Positional embeddings compression factor. Should be set to (context length) / (model's original context length). Equal to 1/rope freq scale. | Gradio | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --listen | Make the web UI reachable from your local network. || --listen-host LISTEN_HOST | The hostname that the server will use. || --listen-port LISTEN_PORT | The listening port that the server will use. || --share | Create a public URL. This is useful for running the web UI on Google Colab or similar. || --auto-launch | Open the web UI in the default browser upon launch. || --gradio-auth USER:PWD | set gradio authentication like "username:password"; or comma-delimit multiple like "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --gradio-auth-path GRADIO_AUTH_PATH | Set the gradio authentication file path. The file should contain one or more user:password pairs in this format: "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --ssl-keyfile SSL_KEYFILE | The path to the SSL certificate key file. || --ssl-certfile SSL_CERTFILE | The path to the SSL certificate cert file. | API | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --api | Enable the API extension. || --public-api | Create a public URL for the API using Cloudfare. || --public-api-id PUBLIC_API_ID | Tunnel ID for named Cloudflare Tunnel. Use together with public-api option. || --api-blocking-port BLOCKING_PORT | The listening port for the blocking API. || --api-streaming-port STREAMING_PORT | The listening port for the streaming API. | Multimodal | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --multimodal-pipeline PIPELINE | The multimodal pipeline to use. Examples: llava-7b , llava-13b . | Presets Inference settings presets can be created under presets/ as yaml files. These files are detected automatically at startup. The presets that are included by default are the result of a contest that received 7215 votes. More details can be found here . Contributing If you would like to contribute to the project, check out the Contributing guidelines . Community Subreddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/oobabooga/ Discord: https://discord.gg/jwZCF2dPQN Acknowledgment In August 2023, Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) provided a generous grant to encourage and support my independent work on this project. I am extremely grateful for their trust and recognition, which will allow me to dedicate more time towards realizing the full potential of text-generation-webui. To restore the repository download the bundle wget https://archive.org/download/github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30/oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30.bundle and run: git clone oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_21-21-30.bundle Source: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui Uploader: oobabooga Upload date: 2023-08-30
“Computational Text Generation : Generation From Data Or Linguistic Structure, Text Planning - Sentence Generation, Explanation Generation : Bibliography” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Computational Text Generation : Generation From Data Or Linguistic Structure, Text Planning - Sentence Generation, Explanation Generation : Bibliography
- Author: Sabourin, Conrad, 1943-
- Language: English
“Computational Text Generation : Generation From Data Or Linguistic Structure, Text Planning - Sentence Generation, Explanation Generation : Bibliography” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ Applied linguistics -- Bibliography - Computational linguistics -- Bibliography - Expert systems (Computer science) -- Bibliography - Natural language processing (Computer science) -- Bibliography - Systemic grammar -- Bibliography - Written communication -- Data processing -- Bibliography
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: computationaltex0000sabo
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 1668.53 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 40 times, the file-s went public at Thu May 02 2019.
Available formats:
ACS Encrypted EPUB - ACS Encrypted PDF - Abbyy GZ - Cloth Cover Detection Log - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Dublin Core - EPUB - Item Tile - JPEG Thumb - JSON - LCP Encrypted EPUB - LCP Encrypted PDF - Log - MARC - MARC Binary - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - PNG - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Original JP2 Tar - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - Title Page Detection Log - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Computational Text Generation : Generation From Data Or Linguistic Structure, Text Planning - Sentence Generation, Explanation Generation : Bibliography at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
8Neural Question Generation From Text: A Preliminary Study
By Qingyu Zhou, Nan Yang, Furu Wei, Chuanqi Tan, Hangbo Bao and Ming Zhou
Automatic question generation aims to generate questions from a text passage where the generated questions can be answered by certain sub-spans of the given passage. Traditional methods mainly use rigid heuristic rules to transform a sentence into related questions. In this work, we propose to apply the neural encoder-decoder model to generate meaningful and diverse questions from natural language sentences. The encoder reads the input text and the answer position, to produce an answer-aware input representation, which is fed to the decoder to generate an answer focused question. We conduct a preliminary study on neural question generation from text with the SQuAD dataset, and the experiment results show that our method can produce fluent and diverse questions.
“Neural Question Generation From Text: A Preliminary Study” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Neural Question Generation From Text: A Preliminary Study
- Authors: ➤ Qingyu ZhouNan YangFuru WeiChuanqi TanHangbo BaoMing Zhou
“Neural Question Generation From Text: A Preliminary Study” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-1704.01792
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 0.46 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 33 times, the file-s went public at Sat Jun 30 2018.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Metadata - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Neural Question Generation From Text: A Preliminary Study at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
9Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - There's No Denying That Since @realDonaldTrump Took Office, @NATO Has Been Significantly Stronger. The President Secured $130 BILLION In New NATO Defense Spending - The Largest Increase In NATO Funding In A Generation! #NATOLondon
By Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
There's no denying that since @realDonaldTrump took office, @NATO has been significantly stronger. The president secured $130 BILLION in new NATO defense spending - the largest increase in NATO funding in a generation! #NATOLondon https://t.co/osE1kI7CrS Source: https://twitter.com/TeamTrump/status/1201949419131883521 Uploader: Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
“Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - There's No Denying That Since @realDonaldTrump Took Office, @NATO Has Been Significantly Stronger. The President Secured $130 BILLION In New NATO Defense Spending - The Largest Increase In NATO Funding In A Generation! #NATOLondon” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - There's No Denying That Since @realDonaldTrump Took Office, @NATO Has Been Significantly Stronger. The President Secured $130 BILLION In New NATO Defense Spending - The Largest Increase In NATO Funding In A Generation! #NATOLondon
- Author: ➤ Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
“Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - There's No Denying That Since @realDonaldTrump Took Office, @NATO Has Been Significantly Stronger. The President Secured $130 BILLION In New NATO Defense Spending - The Largest Increase In NATO Funding In A Generation! #NATOLondon” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: Twitter - video - NATOLondon
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: twitter-1201949419131883521
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "movies" format, the size of the file-s is: 10.25 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 15 times, the file-s went public at Fri Nov 06 2020.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - JPEG - JPEG Thumb - JSON - MPEG4 - Metadata - Thumbnail - Unknown -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - There's No Denying That Since @realDonaldTrump Took Office, @NATO Has Been Significantly Stronger. The President Secured $130 BILLION In New NATO Defense Spending - The Largest Increase In NATO Funding In A Generation! #NATOLondon at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
10Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - Vice President @Mike_Pence: Young People Are The Pro-life Generation #ProLifeVoicesForTrump
By Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
Vice President @Mike_Pence: Young people are the pro-life generation #ProLifeVoicesForTrump https://t.co/hFlA6ZumGx Source: https://twitter.com/TeamTrump/status/1291081819417464832 Uploader: Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
“Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - Vice President @Mike_Pence: Young People Are The Pro-life Generation #ProLifeVoicesForTrump” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - Vice President @Mike_Pence: Young People Are The Pro-life Generation #ProLifeVoicesForTrump
- Author: ➤ Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
“Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - Vice President @Mike_Pence: Young People Are The Pro-life Generation #ProLifeVoicesForTrump” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: Twitter - video - ProLifeVoicesForTrump
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: twitter-1291081819417464832
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "movies" format, the size of the file-s is: 2.69 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 10 times, the file-s went public at Wed Nov 04 2020.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - JPEG - JPEG Thumb - JSON - MPEG4 - Metadata - Thumbnail - Unknown -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - Vice President @Mike_Pence: Young People Are The Pro-life Generation #ProLifeVoicesForTrump at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
11Secrets Of The Rival's Loss Text (Generation I)
By ChickasaurusGL
In this video gameplay is shown on the left side of the screen, and annotations are shown on the right side of the screen. As usual there is a video description as well (below) In Pokémon Red, Blue and Yellow; if you lose against the first battle against the Rival in Professor Oak's laboratory, he will say "Yeah! Am I great or what?" and the game will continue without the player blacking out. If you lose against the second Blue (from Route 22) and the third (in Route 24 north of Cerulean City), he will also say "Yeah! Am I great or what?" but you will black out and be sent to the last Pokémon Center. The other five Blue (which include S.S. Anne Blue, Pokémon Tower Blue, Silph Co. Blue, Route 22 Blue battle #2, Champion Blue at the Pokémon League) give no text when they defeat you. The reason why the Blue from Professor Oak's lab, the first Route 22 Blue and the Route 24 Blue all give the "Yeah! Am I great or what?" text and the others do not is possibly because the first three Blue are part of Trainer class and picture E1. The other five Blue are technically different Trainer classes (F2 and F3) with different pictures. A Blue E1 encountered with the Ditto trick/Trainer escape glitch with a Special stat of 225 will also say "Yeah! Am I great or what?" when he is defeated, whereas a Blue E1 encountered with the old man trick in Red/Blue (requiring a Pk character in slot 3, 5 or 7) will say nothing after winning for unknown reasons; however the fact that the wild Pokémon battle theme plays instead of the Trainer battle theme may have something to do with it. Pokémon Red, Green, Blue and Yellow include seemingly unused texts for when the Rival defeats the player at places other than Professor Oak's laboratory, which include: Possibly the first Route 22 battle - (RIVAL): What? Why do I have 2 POKéMON? You should catch some more too! ; includes a new line error after "catch", where "some more" too is moved to a new line at the bottom of the message box with space above. Possibly the Cerulean City battle - Heh! You're no match for my genius! Possibly the S.S. Anne battle - (PLAYER)! What are you, seasick? You should shape up, pal! Possibly the Pokémon Tower battle - (RIVAL): Well, look at all your wimpy POKéMON! Toughen them up a bit more! Possibly the Silph Co. battle - (RIVAL): How can I put this? You're not good enough to play with us big boys! Possibly the second Route 22 battle - (RIVAL): Hahaha! (PLAYER)! That's your best? You're nowhere near as good as me, pal! Go train some more! You loser! Possibly the Champion Blue battle at the Pokémon League - Hahaha! I won, I won! I'm too good for you, (PLAYER)! You did well to even reach me, (RIVAL), the POKéMON genius! Nice try, loser! Hahaha! Offsets from Red: 0954E4: "Yeah! Am I great or what?"/Oak's lab (25:54E4) 092410: "2 Pokémon" loss text/Route 22 (1) (24:6410) 0A4DE3: 'Heh! No match for my genius!'/Cerulean City (29:4DE3) 080E81: Seasick text/S.S. Anne (20:4E81) 099614: 'Wimpy Pokémon'/Pokémon Tower (26:5614) 084975: 'Big boys'/Silph Co. (21:4975) 0925A0: 'Nowhere near as good as me'/Route 22 (2) (24:65A0) 0862B4: 'Nice try, loser!'/Champion Blue at Pokémon League (21:62B4) In Pokémon Red (and possibly Blue), these texts can be accessed using arbitrary code execution e.g. via "8F" (this requires a Pokémon bootstrap code such as the one found here http://forums.glitchcity.info/index.php/topic,6638.msg194471.html#msg194471) ;and the following code from item 3 (items with quantities greater than 99 can be obtained with the old man trick http://glitchcity.info/wiki/index.php/Old_man_trick or Celadon looping map trick http://glitchcity.info/wiki/index.php/Celadon_looping_map_trick) Lemonade x (pointer byte 1) TM24 x 184 Carbos x (pointer byte 2) X Accuracy x (pointer byte 3) TM05 x 73 Fresh Water x 201 Example: If we want the unused Champion Blue text; the Lemonade must have a quantity of 0x21 (x33 in decimal), the Carbos must have a quantity of 0x62 (x98 in decimal) and the X Accuracy must have a quantity of 0xB4 (x180 in decimal). As raw code this is: ld a,(pointer byte 1; e.g. hex:24) ld (ffb8),a ld h,(pointer byte 2; e.g. hex:64) ld l,(pointer byte 3; e.g. hex:10) call 3c49 ret As raw data this is: 3E xx E0 B8 26 yy 2E zz CD 49 3C C9 Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RPODy8j27Dw Uploader: ChickasaurusGL Upload date: 2016-07-15
“Secrets Of The Rival's Loss Text (Generation I)” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Secrets Of The Rival's Loss Text (Generation I)
- Author: ChickasaurusGL
“Secrets Of The Rival's Loss Text (Generation I)” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ Youtube - video - Gaming - Pokémon - Red - Blue - Yellow - glitch - bug - ピカチュー - バグ - 赤 - 緑 - 青 - ポケモン - ポケットモンスター
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: youtube-RPODy8j27Dw
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "movies" format, the size of the file-s is: 118.80 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 112 times, the file-s went public at Fri Jun 02 2017.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - JPEG - JPEG Thumb - JSON - MPEG4 - Metadata - Ogg Video - Thumbnail - Unknown -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Secrets Of The Rival's Loss Text (Generation I) at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
12Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-28_21-02-24
By oobabooga
A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Supports transformers, GPTQ, llama.cpp (ggml/gguf), Llama models. Text generation web UI A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Its goal is to become the AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui of text generation. | | ||:---:|:---:|| | | Features 3 interface modes: default (two columns), notebook, and chat Multiple model backends: transformers , llama.cpp , ExLlama , AutoGPTQ , GPTQ-for-LLaMa , ctransformers Dropdown menu for quickly switching between different models LoRA: load and unload LoRAs on the fly, train a new LoRA using QLoRA Precise instruction templates for chat mode, including Llama-2-chat, Alpaca, Vicuna, WizardLM, StableLM, and many others 4-bit, 8-bit, and CPU inference through the transformers library Use llama.cpp models with transformers samplers ( llamacpp_HF loader) Multimodal pipelines, including LLaVA and MiniGPT-4 Extensions framework Custom chat characters Very efficient text streaming Markdown output with LaTeX rendering, to use for instance with GALACTICA API, including endpoints for websocket streaming ( see the examples ) To learn how to use the various features, check out the Documentation: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui/tree/main/docs Installation One-click installers | Windows | Linux | macOS | WSL ||--------|--------|--------|--------|| oobabooga-windows.zip | oobabooga-linux.zip | oobabooga-macos.zip | oobabooga-wsl.zip | Just download the zip above, extract it, and double-click on "start". The web UI and all its dependencies will be installed in the same folder. The source codes and more information can be found here: https://github.com/oobabooga/one-click-installers There is no need to run the installers as admin. Huge thanks to @jllllll , @ClayShoaf , and @xNul for their contributions to these installers. Manual installation using Conda Recommended if you have some experience with the command-line. 0. Install Conda https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html On Linux or WSL, it can be automatically installed with these two commands ( source ): curl -sL "https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh" > "Miniconda3.sh"bash Miniconda3.sh 1. Create a new conda environment conda create -n textgen python=3.10.9conda activate textgen 2. Install Pytorch | System | GPU | Command ||--------|---------|---------|| Linux/WSL | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Linux/WSL | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu || Linux | AMD | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm5.4.2 || MacOS + MPS | Any | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Windows | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu117 || Windows | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio | The up-to-date commands can be found here: https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/. 2.1 Additional information MacOS users: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui/pull/393 AMD users: https://rentry.org/eq3hg 3. Install the web UI git clone https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webuicd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt llama.cpp on AMD, Metal, and some specific CPUs Precompiled wheels are included for CPU-only and NVIDIA GPUs (cuBLAS). For AMD, Metal, and some specific CPUs, you need to uninstall those wheels and compile llama-cpp-python yourself. To uninstall: pip uninstall -y llama-cpp-python llama-cpp-python-cuda To compile: https://github.com/abetlen/llama-cpp-python#installation-with-openblas--cublas--clblast--metal bitsandbytes on older NVIDIA GPUs bitsandbytes >= 0.39 may not work. In that case, to use --load-in-8bit , you may have to downgrade like this: Linux: pip install bitsandbytes==0.38.1 Windows: pip install https://github.com/jllllll/bitsandbytes-windows-webui/raw/main/bitsandbytes-0.38.1-py3-none-any.whl Alternative: Docker ```ln -s docker/{Dockerfile,docker-compose.yml,.dockerignore} .cp docker/.env.example .env Edit .env and set TORCH CUDA ARCH_LIST based on your GPU model docker compose up --build``` You need to have docker compose v2.17 or higher installed. See this guide for instructions. For additional docker files, check out this repository . Updating the requirements From time to time, the requirements.txt changes. To update, use these commands: conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt --upgrade Downloading models Models should be placed in the text-generation-webui/models folder. They are usually downloaded from Hugging Face . Transformers or GPTQ models are made of several files and must be placed in a subfolder. Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── lmsys_vicuna-33b-v1.3│ │ ├── config.json│ │ ├── generation_config.json│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00001-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00002-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00003-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00004-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00005-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00006-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00007-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model.bin.index.json│ │ ├── special_tokens_map.json│ │ ├── tokenizer_config.json│ │ └── tokenizer.model In the "Model" tab of the UI, those models can be automatically downloaded from Hugging Face. You can also download them via the command-line with python download-model.py organization/model . GGML/GGUF models are a single file and should be placed directly into models . Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── llama-13b.ggmlv3.q4_K_M.bin Those models must be downloaded manually, as they are not currently supported by the automated downloader. GPT-4chan Instructions GPT-4chan has been shut down from Hugging Face, so you need to download it elsewhere. You have two options: Torrent: 16-bit / 32-bit Direct download: 16-bit / 32-bit The 32-bit version is only relevant if you intend to run the model in CPU mode. Otherwise, you should use the 16-bit version. After downloading the model, follow these steps: Place the files under models/gpt4chan_model_float16 or models/gpt4chan_model . Place GPT-J 6B's config.json file in that same folder: config.json . Download GPT-J 6B's tokenizer files (they will be automatically detected when you attempt to load GPT-4chan): python download-model.py EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B --text-only When you load this model in default or notebook modes, the "HTML" tab will show the generated text in 4chan format: Starting the web UI conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipython server.py Then browse to http://localhost:7860/?__theme=dark Optionally, you can use the following command-line flags: Basic settings | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| -h , --help | Show this help message and exit. || --multi-user | Multi-user mode. Chat histories are not saved or automatically loaded. WARNING: this is highly experimental. || --character CHARACTER | The name of the character to load in chat mode by default. || --model MODEL | Name of the model to load by default. || --lora LORA [LORA ...] | The list of LoRAs to load. If you want to load more than one LoRA, write the names separated by spaces. || --model-dir MODEL_DIR | Path to directory with all the models. || --lora-dir LORA_DIR | Path to directory with all the loras. || --model-menu | Show a model menu in the terminal when the web UI is first launched. || --settings SETTINGS_FILE | Load the default interface settings from this yaml file. See settings-template.yaml for an example. If you create a file called settings.yaml , this file will be loaded by default without the need to use the --settings flag. || --extensions EXTENSIONS [EXTENSIONS ...] | The list of extensions to load. If you want to load more than one extension, write the names separated by spaces. || --verbose | Print the prompts to the terminal. | Model loader | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| --loader LOADER | Choose the model loader manually, otherwise, it will get autodetected. Valid options: transformers, autogptq, gptq-for-llama, exllama, exllama_hf, llamacpp, rwkv, ctransformers | Accelerate/transformers | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --cpu | Use the CPU to generate text. Warning: Training on CPU is extremely slow.|| --auto-devices | Automatically split the model across the available GPU(s) and CPU. || --gpu-memory GPU_MEMORY [GPU_MEMORY ...] | Maximum GPU memory in GiB to be allocated per GPU. Example: --gpu-memory 10 for a single GPU, --gpu-memory 10 5 for two GPUs. You can also set values in MiB like --gpu-memory 3500MiB . || --cpu-memory CPU_MEMORY | Maximum CPU memory in GiB to allocate for offloaded weights. Same as above.|| --disk | If the model is too large for your GPU(s) and CPU combined, send the remaining layers to the disk. || --disk-cache-dir DISK_CACHE_DIR | Directory to save the disk cache to. Defaults to cache/ . || --load-in-8bit | Load the model with 8-bit precision (using bitsandbytes).|| --bf16 | Load the model with bfloat16 precision. Requires NVIDIA Ampere GPU. || --no-cache | Set use_cache to False while generating text. This reduces the VRAM usage a bit with a performance cost. || --xformers | Use xformer's memory efficient attention. This should increase your tokens/s. || --sdp-attention | Use torch 2.0's sdp attention. || --trust-remote-code | Set trust remote code=True while loading a model. Necessary for ChatGLM and Falcon. | Accelerate 4-bit ⚠️ Requires minimum compute of 7.0 on Windows at the moment. | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --load-in-4bit | Load the model with 4-bit precision (using bitsandbytes). || --compute_dtype COMPUTE_DTYPE | compute dtype for 4-bit. Valid options: bfloat16, float16, float32. || --quant_type QUANT_TYPE | quant type for 4-bit. Valid options: nf4, fp4. || --use_double_quant | use double_quant for 4-bit. | GGML/GGUF (for llama.cpp and ctransformers) | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --threads | Number of threads to use. || --n_batch | Maximum number of prompt tokens to batch together when calling llama_eval. || --n-gpu-layers N_GPU_LAYERS | Number of layers to offload to the GPU. Only works if llama-cpp-python was compiled with BLAS. Set this to 1000000000 to offload all layers to the GPU. || --n_ctx N_CTX | Size of the prompt context. | llama.cpp | Flag | Description ||---------------|---------------|| --no-mmap | Prevent mmap from being used. || --mlock | Force the system to keep the model in RAM. || --mul_mat_q | Activate new mulmat kernels. || --cache-capacity CACHE_CAPACITY | Maximum cache capacity. Examples: 2000MiB, 2GiB. When provided without units, bytes will be assumed. || --tensor_split TENSOR_SPLIT | Split the model across multiple GPUs, comma-separated list of proportions, e.g. 18,17 || --llama_cpp_seed SEED | Seed for llama-cpp models. Default 0 (random). || --n_gqa N_GQA | GGML only (not used by GGUF): Grouped-Query Attention. Must be 8 for llama-2 70b. || --rms_norm_eps RMS_NORM_EPS | GGML only (not used by GGUF): 5e-6 is a good value for llama-2 models. || --cpu | Use the CPU version of llama-cpp-python instead of the GPU-accelerated version. || --cfg-cache | llamacpp_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. | ctransformers | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently gpt2, gptj, gptneox, falcon, llama, mpt, starcoder (gptbigcode), dollyv2, and replit are supported. | AutoGPTQ | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --triton | Use triton. || --no_inject_fused_attention | Disable the use of fused attention, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_inject_fused_mlp | Triton mode only: disable the use of fused MLP, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_use_cuda_fp16 | This can make models faster on some systems. || --desc_act | For models that don't have a quantize config.json, this parameter is used to define whether to set desc act or not in BaseQuantizeConfig. || --disable_exllama | Disable ExLlama kernel, which can improve inference speed on some systems. | ExLlama | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --gpu-split | Comma-separated list of VRAM (in GB) to use per GPU device for model layers, e.g. 20,7,7 || --max_seq_len MAX_SEQ_LEN | Maximum sequence length. || --cfg-cache | ExLlama_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. Necessary to use CFG with that loader, but not necessary for CFG with base ExLlama. | GPTQ-for-LLaMa | Flag | Description ||---------------------------|-------------|| --wbits WBITS | Load a pre-quantized model with specified precision in bits. 2, 3, 4 and 8 are supported. || --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently LLaMA, OPT, and GPT-J are supported. || --groupsize GROUPSIZE | Group size. || --pre_layer PRE_LAYER [PRE_LAYER ...] | The number of layers to allocate to the GPU. Setting this parameter enables CPU offloading for 4-bit models. For multi-gpu, write the numbers separated by spaces, eg --pre_layer 30 60 . || --checkpoint CHECKPOINT | The path to the quantized checkpoint file. If not specified, it will be automatically detected. || --monkey-patch | Apply the monkey patch for using LoRAs with quantized models. DeepSpeed | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --deepspeed | Enable the use of DeepSpeed ZeRO-3 for inference via the Transformers integration. || --nvme-offload-dir NVME_OFFLOAD_DIR | DeepSpeed: Directory to use for ZeRO-3 NVME offloading. || --local_rank LOCAL_RANK | DeepSpeed: Optional argument for distributed setups. | RWKV | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------|-------------|| --rwkv-strategy RWKV_STRATEGY | RWKV: The strategy to use while loading the model. Examples: "cpu fp32", "cuda fp16", "cuda fp16i8". || --rwkv-cuda-on | RWKV: Compile the CUDA kernel for better performance. | RoPE (for llama.cpp, ExLlama, and transformers) | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --alpha_value ALPHA_VALUE | Positional embeddings alpha factor for NTK RoPE scaling. Use either this or compress pos emb, not both. || --rope_freq_base ROPE_FREQ_BASE | If greater than 0, will be used instead of alpha value. Those two are related by rope freq base = 10000 * alpha value ^ (64 / 63). || --compress_pos_emb COMPRESS_POS_EMB | Positional embeddings compression factor. Should be set to (context length) / (model's original context length). Equal to 1/rope freq scale. | Gradio | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --listen | Make the web UI reachable from your local network. || --listen-host LISTEN_HOST | The hostname that the server will use. || --listen-port LISTEN_PORT | The listening port that the server will use. || --share | Create a public URL. This is useful for running the web UI on Google Colab or similar. || --auto-launch | Open the web UI in the default browser upon launch. || --gradio-auth USER:PWD | set gradio authentication like "username:password"; or comma-delimit multiple like "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --gradio-auth-path GRADIO_AUTH_PATH | Set the gradio authentication file path. The file should contain one or more user:password pairs in this format: "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --ssl-keyfile SSL_KEYFILE | The path to the SSL certificate key file. || --ssl-certfile SSL_CERTFILE | The path to the SSL certificate cert file. | API | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --api | Enable the API extension. || --public-api | Create a public URL for the API using Cloudfare. || --public-api-id PUBLIC_API_ID | Tunnel ID for named Cloudflare Tunnel. Use together with public-api option. || --api-blocking-port BLOCKING_PORT | The listening port for the blocking API. || --api-streaming-port STREAMING_PORT | The listening port for the streaming API. | Multimodal | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --multimodal-pipeline PIPELINE | The multimodal pipeline to use. Examples: llava-7b , llava-13b . | Presets Inference settings presets can be created under presets/ as yaml files. These files are detected automatically at startup. The presets that are included by default are the result of a contest that received 7215 votes. More details can be found here . Contributing If you would like to contribute to the project, check out the Contributing guidelines . Community Subreddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/oobabooga/ Discord: https://discord.gg/jwZCF2dPQN Acknowledgment In August 2023, Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) provided a generous grant to encourage and support my independent work on this project. I am extremely grateful for their trust and recognition, which will allow me to dedicate more time towards realizing the full potential of text-generation-webui. To restore the repository download the bundle wget https://archive.org/download/github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-28_21-02-24/oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-28_21-02-24.bundle and run: git clone oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-28_21-02-24.bundle Source: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui Uploader: oobabooga Upload date: 2023-08-28
“Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-28_21-02-24” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-28_21-02-24
- Author: oobabooga
“Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-28_21-02-24” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ➤ github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-28_21-02-24
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "software" format, the size of the file-s is: 3.96 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 976 times, the file-s went public at Mon Aug 28 2023.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - JPEG - JPEG Thumb - Metadata - Unknown -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-28_21-02-24 at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
13BSTJ 62: 10. December 1983: Generation Of Syntax-Directed Editors With Text-Oriented Features. (Bottos, B.A.; Kintala, C.M.R.)
Bell System Technical Journal, 62: 10. December 1983 pp 3205-3224. Generation of Syntax-Directed Editors With Text-Oriented Features. (Bottos, B.A.; Kintala, C.M.R.)
“BSTJ 62: 10. December 1983: Generation Of Syntax-Directed Editors With Text-Oriented Features. (Bottos, B.A.; Kintala, C.M.R.)” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ BSTJ 62: 10. December 1983: Generation Of Syntax-Directed Editors With Text-Oriented Features. (Bottos, B.A.; Kintala, C.M.R.)
- Language: English
“BSTJ 62: 10. December 1983: Generation Of Syntax-Directed Editors With Text-Oriented Features. (Bottos, B.A.; Kintala, C.M.R.)” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ nonterminal - parser - program - grammar - specification - production - editor - input - editors - programmer - parser generator - grammar specification - system technical - age grammar - hybrid editor - input string - computer science - production rule - bell system - current nonterminal
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: bstj62-10-3205
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 17.65 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 304 times, the file-s went public at Sat Jan 19 2013.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Additional Text PDF - Animated GIF - Archive BitTorrent - DjVu - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Image Container PDF - Item Tile - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find BSTJ 62: 10. December 1983: Generation Of Syntax-Directed Editors With Text-Oriented Features. (Bottos, B.A.; Kintala, C.M.R.) at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
14DTIC ADA125253: Nigel: A Systemic Grammar For Text Generation.
By Defense Technical Information Center
Programming a computer to write text which meets a prior need is a challenging research task. As part of such research, Nigel, a large programmed grammar of English, has been created in the framework of systemic linguistics begun by Halliday. In addition to specifying function and structures of English, Nigel has a novel semantic stratum which specifies the situations in which each grammatical feature should be used. The report consists of three papers on Nigel: an introductory overview, the script of a demonstration of its use in generation, and an exposition of how Nigel relates to the systemic framework. Although the effort to develop Nigel is significant both as computer science research and as linguistic inquiry the outlook of the report is oriented to its linguistic significance.
“DTIC ADA125253: Nigel: A Systemic Grammar For Text Generation.” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA125253: Nigel: A Systemic Grammar For Text Generation.
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA125253: Nigel: A Systemic Grammar For Text Generation.” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Mann,William C - UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA MARINA DEL REY INFORMATION SCIENCES INST - *COMPUTER PROGRAMMING - COMPUTER PROGRAM DOCUMENTATION - SYSTEMS ENGINEERING - NETWORKS - PROGRAMMING LANGUAGES - SEMANTICS - STRUCTURES - INFORMATION RETRIEVAL - ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE - NETWORK ANALYSIS(MANAGEMENT) - SYNTAX - LINGUISTICS - TEXT PROCESSING - PARSERS - GRAMMARS - ENGLISH LANGUAGE
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA125253
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 55.48 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 109 times, the file-s went public at Wed Jan 10 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA125253: Nigel: A Systemic Grammar For Text Generation. at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
15DTIC ADA224689: From Systemic-Functional Grammar To Systemic-Functional Text Generation: Escalating The Exchange
By Defense Technical Information Center
The boundaries between planning and realization within generation are a standard division in a natural language processing, although they no longer seem so secure. New territorial divisions appear necessary, but it is still unclear where the borders are best drawn. This report shows that systemic- functional linguistics (SFL) offers a rich body of linguistic work concerned precisely with issues that are coming to the forefront in natural language processing. This work provides theoretically well-motivated and thorough guidance in an area where text planning and generation are still lacking in experience: the treatment of text in context for the purposes of communication and social interaction. Many of the issues raised in text planning are also addressed within the SFL tradition; SFL can provide an extremely detailed and beneficial map of the territory through which we now need to move. Keywords: Computational systemic linguistics, Text generation, Text planning.
“DTIC ADA224689: From Systemic-Functional Grammar To Systemic-Functional Text Generation: Escalating The Exchange” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA224689: From Systemic-Functional Grammar To Systemic-Functional Text Generation: Escalating The Exchange
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA224689: From Systemic-Functional Grammar To Systemic-Functional Text Generation: Escalating The Exchange” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Bateman, John A - UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA MARINA DEL REY INFORMATION SCIENCES INST - *NATURAL LANGUAGE - *COMPUTATIONAL LINGUISTICS - INFORMATION PROCESSING - HUMAN RELATIONS - LINGUISTICS
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA224689
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 12.56 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 67 times, the file-s went public at Mon Feb 26 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA224689: From Systemic-Functional Grammar To Systemic-Functional Text Generation: Escalating The Exchange at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
16DTIC ADA199749: Unidirectional Spectral Wave Generation And Analysis In Wave Basins. Volume 1. Main Text And Appendix A
By Defense Technical Information Center
A series of 36 unidirectional spectral waves was generated to determine the relationship between wave generator control signal and measured response at seven locations in teh model basin. Control signals consisted of combinations of three peak periods ranging from 1.0 to 2.0 sec, two zero-moment wave heights from 1 to 3 in., three spectral peak enhancement factors from 3.3 to 15, and two peak directions of 0 and -30 deg. Seven resistance or capacitance wave gages were centrally located 20 ft in front of the wave generator about its center line in a combination cross and 2-3-1-7 linear array. Descriptions of the spectral simulation and generation, time series and spectral analysis, frequency response, and wave grouping analysis are presented. Comparisons of predicted and measured peak period, zero-moment wave height, peak wave direction, frequency spectra, and directional spreading are presented and discussed. Frequency response and wave grouping statistics are calculated for each test case. This report consists of two volumes: Volume I consisting of the main test and Appendix A and Volume II consisting of Appendixes B-H.
“DTIC ADA199749: Unidirectional Spectral Wave Generation And Analysis In Wave Basins. Volume 1. Main Text And Appendix A” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA199749: Unidirectional Spectral Wave Generation And Analysis In Wave Basins. Volume 1. Main Text And Appendix A
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA199749: Unidirectional Spectral Wave Generation And Analysis In Wave Basins. Volume 1. Main Text And Appendix A” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Briggs, Michael J - COASTAL ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTER VICKSBURG MS - *MODEL BASINS - *WATER WAVES - CONTROL - SIMULATION - PEAK VALUES - STATISTICS - TIME SERIES ANALYSIS - SPECTRA - WAVE PROPAGATION - SIGNALS - GENERATORS - SPECTRUM ANALYSIS - GAGES - FREQUENCY RESPONSE - UNIDIRECTIONAL - WAVE ANALYZERS - TEST AND EVALUATION - FREQUENCY
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA199749
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 38.18 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 84 times, the file-s went public at Wed Feb 21 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA199749: Unidirectional Spectral Wave Generation And Analysis In Wave Basins. Volume 1. Main Text And Appendix A at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
17DTIC ADA460217: Coordinating Text And Graphics In Explanation Generation
By Defense Technical Information Center
To generate multimedia explanations, a system must he able to coordinate the use of different media in a single explanation. In this paper, we present an architecture that we have developed for COMET (COordinated Multimedia Explanation Testbed), a system that generates directions for equipment maintenance and repair, and we show how it addresses the coordination problem. In particular, we focus on the use of a single content planner that produces a common content description used by multiple media-specific generators, a media coordinator that makes a fine-grained division of information between media, and bidirectional interaction between media-specific generators to allow influence across media.
“DTIC ADA460217: Coordinating Text And Graphics In Explanation Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA460217: Coordinating Text And Graphics In Explanation Generation
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA460217: Coordinating Text And Graphics In Explanation Generation” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Feiner, Steven K - COLUMBIA UNIV NEW YORK DEPT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE - *WORDS(LANGUAGE) - *MEDIA - MAINTENANCE - NATURAL LANGUAGE - LINGUISTICS - TEST BEDS - INTERACTIONS
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA460217
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 9.58 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 52 times, the file-s went public at Fri Jun 08 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - JPEG Thumb - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA460217: Coordinating Text And Graphics In Explanation Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
18Emphatic Generation: Employing The Theory Of Semantic Emphasis For Text Generation
By Elke Teich, Beate Firzlaff and John A. Bateman
The paper deals with the problem of text generation and planning approaches making only limited formally specifiable contact with accounts of grammar. We propose an enhancement of a systemically-based generation architecture for German (the KOMET system) by aspects of Kunze's theory of semantic emphasis. Doing this, we gain more control over both concept selection in generation and choice of fine-grained grammatical variation.
“Emphatic Generation: Employing The Theory Of Semantic Emphasis For Text Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Emphatic Generation: Employing The Theory Of Semantic Emphasis For Text Generation
- Authors: Elke TeichBeate FirzlaffJohn A. Bateman
- Language: English
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-cmp-lg9704012
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 7.68 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 110 times, the file-s went public at Sun Sep 22 2013.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Animated GIF - Archive BitTorrent - DjVu - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Emphatic Generation: Employing The Theory Of Semantic Emphasis For Text Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
19Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-29_06-23-16
By oobabooga
A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Supports transformers, GPTQ, llama.cpp (ggml/gguf), Llama models. Text generation web UI A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Its goal is to become the AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui of text generation. | | ||:---:|:---:|| | | Features 3 interface modes: default (two columns), notebook, and chat Multiple model backends: transformers , llama.cpp , ExLlama , AutoGPTQ , GPTQ-for-LLaMa , ctransformers Dropdown menu for quickly switching between different models LoRA: load and unload LoRAs on the fly, train a new LoRA using QLoRA Precise instruction templates for chat mode, including Llama-2-chat, Alpaca, Vicuna, WizardLM, StableLM, and many others 4-bit, 8-bit, and CPU inference through the transformers library Use llama.cpp models with transformers samplers ( llamacpp_HF loader) Multimodal pipelines, including LLaVA and MiniGPT-4 Extensions framework Custom chat characters Very efficient text streaming Markdown output with LaTeX rendering, to use for instance with GALACTICA API, including endpoints for websocket streaming ( see the examples ) To learn how to use the various features, check out the Documentation: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui/tree/main/docs Installation One-click installers | Windows | Linux | macOS | WSL ||--------|--------|--------|--------|| oobabooga-windows.zip | oobabooga-linux.zip | oobabooga-macos.zip | oobabooga-wsl.zip | Just download the zip above, extract it, and double-click on "start". The web UI and all its dependencies will be installed in the same folder. The source codes and more information can be found here: https://github.com/oobabooga/one-click-installers There is no need to run the installers as admin. Huge thanks to @jllllll , @ClayShoaf , and @xNul for their contributions to these installers. Manual installation using Conda Recommended if you have some experience with the command-line. 0. Install Conda https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html On Linux or WSL, it can be automatically installed with these two commands ( source ): curl -sL "https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh" > "Miniconda3.sh"bash Miniconda3.sh 1. Create a new conda environment conda create -n textgen python=3.10.9conda activate textgen 2. Install Pytorch | System | GPU | Command ||--------|---------|---------|| Linux/WSL | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Linux/WSL | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu || Linux | AMD | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm5.4.2 || MacOS + MPS | Any | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Windows | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu117 || Windows | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio | The up-to-date commands can be found here: https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/. 2.1 Additional information MacOS users: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui/pull/393 AMD users: https://rentry.org/eq3hg 3. Install the web UI git clone https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webuicd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt llama.cpp on AMD, Metal, and some specific CPUs Precompiled wheels are included for CPU-only and NVIDIA GPUs (cuBLAS). For AMD, Metal, and some specific CPUs, you need to uninstall those wheels and compile llama-cpp-python yourself. To uninstall: pip uninstall -y llama-cpp-python llama-cpp-python-cuda To compile: https://github.com/abetlen/llama-cpp-python#installation-with-openblas--cublas--clblast--metal bitsandbytes on older NVIDIA GPUs bitsandbytes >= 0.39 may not work. In that case, to use --load-in-8bit , you may have to downgrade like this: Linux: pip install bitsandbytes==0.38.1 Windows: pip install https://github.com/jllllll/bitsandbytes-windows-webui/raw/main/bitsandbytes-0.38.1-py3-none-any.whl Alternative: Docker ```ln -s docker/{Dockerfile,docker-compose.yml,.dockerignore} .cp docker/.env.example .env Edit .env and set TORCH CUDA ARCH_LIST based on your GPU model docker compose up --build``` You need to have docker compose v2.17 or higher installed. See this guide for instructions. For additional docker files, check out this repository . Updating the requirements From time to time, the requirements.txt changes. To update, use these commands: conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt --upgrade Downloading models Models should be placed in the text-generation-webui/models folder. They are usually downloaded from Hugging Face . Transformers or GPTQ models are made of several files and must be placed in a subfolder. Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── lmsys_vicuna-33b-v1.3│ │ ├── config.json│ │ ├── generation_config.json│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00001-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00002-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00003-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00004-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00005-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00006-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00007-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model.bin.index.json│ │ ├── special_tokens_map.json│ │ ├── tokenizer_config.json│ │ └── tokenizer.model In the "Model" tab of the UI, those models can be automatically downloaded from Hugging Face. You can also download them via the command-line with python download-model.py organization/model . GGML/GGUF models are a single file and should be placed directly into models . Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── llama-13b.ggmlv3.q4_K_M.bin Those models must be downloaded manually, as they are not currently supported by the automated downloader. GPT-4chan Instructions GPT-4chan has been shut down from Hugging Face, so you need to download it elsewhere. You have two options: Torrent: 16-bit / 32-bit Direct download: 16-bit / 32-bit The 32-bit version is only relevant if you intend to run the model in CPU mode. Otherwise, you should use the 16-bit version. After downloading the model, follow these steps: Place the files under models/gpt4chan_model_float16 or models/gpt4chan_model . Place GPT-J 6B's config.json file in that same folder: config.json . Download GPT-J 6B's tokenizer files (they will be automatically detected when you attempt to load GPT-4chan): python download-model.py EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B --text-only When you load this model in default or notebook modes, the "HTML" tab will show the generated text in 4chan format: Starting the web UI conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipython server.py Then browse to http://localhost:7860/?__theme=dark Optionally, you can use the following command-line flags: Basic settings | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| -h , --help | Show this help message and exit. || --multi-user | Multi-user mode. Chat histories are not saved or automatically loaded. WARNING: this is highly experimental. || --character CHARACTER | The name of the character to load in chat mode by default. || --model MODEL | Name of the model to load by default. || --lora LORA [LORA ...] | The list of LoRAs to load. If you want to load more than one LoRA, write the names separated by spaces. || --model-dir MODEL_DIR | Path to directory with all the models. || --lora-dir LORA_DIR | Path to directory with all the loras. || --model-menu | Show a model menu in the terminal when the web UI is first launched. || --settings SETTINGS_FILE | Load the default interface settings from this yaml file. See settings-template.yaml for an example. If you create a file called settings.yaml , this file will be loaded by default without the need to use the --settings flag. || --extensions EXTENSIONS [EXTENSIONS ...] | The list of extensions to load. If you want to load more than one extension, write the names separated by spaces. || --verbose | Print the prompts to the terminal. | Model loader | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| --loader LOADER | Choose the model loader manually, otherwise, it will get autodetected. Valid options: transformers, autogptq, gptq-for-llama, exllama, exllama_hf, llamacpp, rwkv, ctransformers | Accelerate/transformers | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --cpu | Use the CPU to generate text. Warning: Training on CPU is extremely slow.|| --auto-devices | Automatically split the model across the available GPU(s) and CPU. || --gpu-memory GPU_MEMORY [GPU_MEMORY ...] | Maximum GPU memory in GiB to be allocated per GPU. Example: --gpu-memory 10 for a single GPU, --gpu-memory 10 5 for two GPUs. You can also set values in MiB like --gpu-memory 3500MiB . || --cpu-memory CPU_MEMORY | Maximum CPU memory in GiB to allocate for offloaded weights. Same as above.|| --disk | If the model is too large for your GPU(s) and CPU combined, send the remaining layers to the disk. || --disk-cache-dir DISK_CACHE_DIR | Directory to save the disk cache to. Defaults to cache/ . || --load-in-8bit | Load the model with 8-bit precision (using bitsandbytes).|| --bf16 | Load the model with bfloat16 precision. Requires NVIDIA Ampere GPU. || --no-cache | Set use_cache to False while generating text. This reduces the VRAM usage a bit with a performance cost. || --xformers | Use xformer's memory efficient attention. This should increase your tokens/s. || --sdp-attention | Use torch 2.0's sdp attention. || --trust-remote-code | Set trust remote code=True while loading a model. Necessary for ChatGLM and Falcon. | Accelerate 4-bit ⚠️ Requires minimum compute of 7.0 on Windows at the moment. | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --load-in-4bit | Load the model with 4-bit precision (using bitsandbytes). || --compute_dtype COMPUTE_DTYPE | compute dtype for 4-bit. Valid options: bfloat16, float16, float32. || --quant_type QUANT_TYPE | quant type for 4-bit. Valid options: nf4, fp4. || --use_double_quant | use double_quant for 4-bit. | GGML/GGUF (for llama.cpp and ctransformers) | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --threads | Number of threads to use. || --n_batch | Maximum number of prompt tokens to batch together when calling llama_eval. || --n-gpu-layers N_GPU_LAYERS | Number of layers to offload to the GPU. Only works if llama-cpp-python was compiled with BLAS. Set this to 1000000000 to offload all layers to the GPU. || --n_ctx N_CTX | Size of the prompt context. | llama.cpp | Flag | Description ||---------------|---------------|| --no-mmap | Prevent mmap from being used. || --mlock | Force the system to keep the model in RAM. || --mul_mat_q | Activate new mulmat kernels. || --cache-capacity CACHE_CAPACITY | Maximum cache capacity. Examples: 2000MiB, 2GiB. When provided without units, bytes will be assumed. || --tensor_split TENSOR_SPLIT | Split the model across multiple GPUs, comma-separated list of proportions, e.g. 18,17 || --llama_cpp_seed SEED | Seed for llama-cpp models. Default 0 (random). || --n_gqa N_GQA | GGML only (not used by GGUF): Grouped-Query Attention. Must be 8 for llama-2 70b. || --rms_norm_eps RMS_NORM_EPS | GGML only (not used by GGUF): 5e-6 is a good value for llama-2 models. || --cpu | Use the CPU version of llama-cpp-python instead of the GPU-accelerated version. || --cfg-cache | llamacpp_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. | ctransformers | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently gpt2, gptj, gptneox, falcon, llama, mpt, starcoder (gptbigcode), dollyv2, and replit are supported. | AutoGPTQ | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --triton | Use triton. || --no_inject_fused_attention | Disable the use of fused attention, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_inject_fused_mlp | Triton mode only: disable the use of fused MLP, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_use_cuda_fp16 | This can make models faster on some systems. || --desc_act | For models that don't have a quantize config.json, this parameter is used to define whether to set desc act or not in BaseQuantizeConfig. || --disable_exllama | Disable ExLlama kernel, which can improve inference speed on some systems. | ExLlama | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --gpu-split | Comma-separated list of VRAM (in GB) to use per GPU device for model layers, e.g. 20,7,7 || --max_seq_len MAX_SEQ_LEN | Maximum sequence length. || --cfg-cache | ExLlama_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. Necessary to use CFG with that loader, but not necessary for CFG with base ExLlama. | GPTQ-for-LLaMa | Flag | Description ||---------------------------|-------------|| --wbits WBITS | Load a pre-quantized model with specified precision in bits. 2, 3, 4 and 8 are supported. || --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently LLaMA, OPT, and GPT-J are supported. || --groupsize GROUPSIZE | Group size. || --pre_layer PRE_LAYER [PRE_LAYER ...] | The number of layers to allocate to the GPU. Setting this parameter enables CPU offloading for 4-bit models. For multi-gpu, write the numbers separated by spaces, eg --pre_layer 30 60 . || --checkpoint CHECKPOINT | The path to the quantized checkpoint file. If not specified, it will be automatically detected. || --monkey-patch | Apply the monkey patch for using LoRAs with quantized models. DeepSpeed | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --deepspeed | Enable the use of DeepSpeed ZeRO-3 for inference via the Transformers integration. || --nvme-offload-dir NVME_OFFLOAD_DIR | DeepSpeed: Directory to use for ZeRO-3 NVME offloading. || --local_rank LOCAL_RANK | DeepSpeed: Optional argument for distributed setups. | RWKV | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------|-------------|| --rwkv-strategy RWKV_STRATEGY | RWKV: The strategy to use while loading the model. Examples: "cpu fp32", "cuda fp16", "cuda fp16i8". || --rwkv-cuda-on | RWKV: Compile the CUDA kernel for better performance. | RoPE (for llama.cpp, ExLlama, and transformers) | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --alpha_value ALPHA_VALUE | Positional embeddings alpha factor for NTK RoPE scaling. Use either this or compress pos emb, not both. || --rope_freq_base ROPE_FREQ_BASE | If greater than 0, will be used instead of alpha value. Those two are related by rope freq base = 10000 * alpha value ^ (64 / 63). || --compress_pos_emb COMPRESS_POS_EMB | Positional embeddings compression factor. Should be set to (context length) / (model's original context length). Equal to 1/rope freq scale. | Gradio | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --listen | Make the web UI reachable from your local network. || --listen-host LISTEN_HOST | The hostname that the server will use. || --listen-port LISTEN_PORT | The listening port that the server will use. || --share | Create a public URL. This is useful for running the web UI on Google Colab or similar. || --auto-launch | Open the web UI in the default browser upon launch. || --gradio-auth USER:PWD | set gradio authentication like "username:password"; or comma-delimit multiple like "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --gradio-auth-path GRADIO_AUTH_PATH | Set the gradio authentication file path. The file should contain one or more user:password pairs in this format: "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --ssl-keyfile SSL_KEYFILE | The path to the SSL certificate key file. || --ssl-certfile SSL_CERTFILE | The path to the SSL certificate cert file. | API | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --api | Enable the API extension. || --public-api | Create a public URL for the API using Cloudfare. || --public-api-id PUBLIC_API_ID | Tunnel ID for named Cloudflare Tunnel. Use together with public-api option. || --api-blocking-port BLOCKING_PORT | The listening port for the blocking API. || --api-streaming-port STREAMING_PORT | The listening port for the streaming API. | Multimodal | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --multimodal-pipeline PIPELINE | The multimodal pipeline to use. Examples: llava-7b , llava-13b . | Presets Inference settings presets can be created under presets/ as yaml files. These files are detected automatically at startup. The presets that are included by default are the result of a contest that received 7215 votes. More details can be found here . Contributing If you would like to contribute to the project, check out the Contributing guidelines . Community Subreddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/oobabooga/ Discord: https://discord.gg/jwZCF2dPQN Acknowledgment In August 2023, Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) provided a generous grant to encourage and support my independent work on this project. I am extremely grateful for their trust and recognition, which will allow me to dedicate more time towards realizing the full potential of text-generation-webui. To restore the repository download the bundle wget https://archive.org/download/github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-29_06-23-16/oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-29_06-23-16.bundle and run: git clone oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-29_06-23-16.bundle Source: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui Uploader: oobabooga Upload date: 2023-08-29
“Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-29_06-23-16” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-29_06-23-16
- Author: oobabooga
“Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-29_06-23-16” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ➤ github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-29_06-23-16
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "software" format, the size of the file-s is: 3.97 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 179 times, the file-s went public at Tue Aug 29 2023.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - JPEG - JPEG Thumb - Metadata - Unknown -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-29_06-23-16 at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
20Deep Learning For X Ray Image To Text Generation
By Mahima Chaddha | Sneha Kashid | Snehal Bhosale | Prof. Radha Deoghare
Motivated by the recent success of supervised and weakly supervised common object discovery, in this work we move forward one step further to tackle common object discovery in a fully unsupervised way. Mainly, object co localization aims at simultaneously localizing the objects of the same class across a group of images. Traditional object localization detection usually trains the specific object detectors which require bounding box annotations of object instances, or at least image level labels to indicate the presence absence of objects in an image. Given a collection of images without any annotations, our proposed fully unsupervised method is to simultaneously discover images that contain common objects and also localize common objects in corresponding images. It has been long envisioned that the machines one day will understand the visual world at a human level of intelligence. Now we can build very deep convolutional neural networks CNNs and achieve an impressively low error rate for tasks like large scale image classification. However, in tasks like image classification, the content of an image is usually simple, containing a predominant object to be classified. The situation could be much more challenging when we want computers to understand complex scenes. Image captioning is one such task. In these tasks, we have to train a model to predict the category of a given x ray image is to first annotate each x ray image in a training set with a label from the predefined set of categories. Through such fully supervised training, the computer learns how to classify an x ray image and convert into text. by Mahima Chaddha | Sneha Kashid | Snehal Bhosale | Prof. Radha Deoghare "Deep Learning for X-ray Image to Text Generation" Published in International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (ijtsrd), ISSN: 2456-6470, Volume-3 | Issue-3, April 2019, URL: https://www.ijtsrd.com/papers/ijtsrd23168.pdf Paper URL: https://www.ijtsrd.com/engineering/information-technology/23168/deep-learning-for-x-ray-image-to-text-generation/mahima-chaddha
“Deep Learning For X Ray Image To Text Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Deep Learning For X Ray Image To Text Generation
- Author: ➤ Mahima Chaddha | Sneha Kashid | Snehal Bhosale | Prof. Radha Deoghare
- Language: English
“Deep Learning For X Ray Image To Text Generation” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ Information Technology - object detection - object tracking - object identification - edge detection - convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ➤ Httpswww.ijtsrd.comengineeringinformation-technology23168deep-learning-for-x-ray
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 4.03 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 95 times, the file-s went public at Sat Jun 08 2019.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Deep Learning For X Ray Image To Text Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
21Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - President @realDonaldTrump: The Biden Lockdown Will Result In Countless Deaths, Destroy Millions Of Small Businesses And Wipe Out An Entire Generation Of Hopes And Dreams
By Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
President @realDonaldTrump: The Biden Lockdown will result in countless deaths, destroy millions of small businesses and wipe out an entire generation of hopes and dreams https://t.co/KaZvJIdeWF Source: https://twitter.com/TeamTrump/status/1323001620154720266 Uploader: Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
“Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - President @realDonaldTrump: The Biden Lockdown Will Result In Countless Deaths, Destroy Millions Of Small Businesses And Wipe Out An Entire Generation Of Hopes And Dreams” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - President @realDonaldTrump: The Biden Lockdown Will Result In Countless Deaths, Destroy Millions Of Small Businesses And Wipe Out An Entire Generation Of Hopes And Dreams
- Author: ➤ Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
“Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - President @realDonaldTrump: The Biden Lockdown Will Result In Countless Deaths, Destroy Millions Of Small Businesses And Wipe Out An Entire Generation Of Hopes And Dreams” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: twitter-1323001620154720266
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "movies" format, the size of the file-s is: 8.15 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 9 times, the file-s went public at Mon Nov 02 2020.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - JPEG - JPEG Thumb - JSON - MPEG4 - Metadata - Thumbnail - Unknown -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - President @realDonaldTrump: The Biden Lockdown Will Result In Countless Deaths, Destroy Millions Of Small Businesses And Wipe Out An Entire Generation Of Hopes And Dreams at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
22ERIC ED099200: The Enviornmental Impact Of Electrical Power Generation: Nuclear And Fossil. A Minicourse For Secondary Schools And Adult Education. Text.
By ERIC
This course, developed for use in secondary and adult education, is an effort to describe the cost-benefit ratio of the various methods of generation of electrical power in an era when the requirement for additional sources of power is growing at an ever-increasing rate and environmental protection is a major concern. This course was written and compiled by an independent committee drawn from educators, engineers, health physicists, members of industry and conservation groups, and environmental scientists. Among the topics discussed are the increasing need for electrical power and methods for meeting this need, nuclear power and fossil fueled plants, the biological effects of nuclear and fossil fueled plants, wastes in the production of electric power, plant site considerations, energy conservation, and the environmental effects of electrical power generation. The appendixes include a glossary of terms, a bibliography, a decision-making model and a brief outline of the procedures which must be followed by a utility in order to construct and operate a nuclear power plant. (BT)
“ERIC ED099200: The Enviornmental Impact Of Electrical Power Generation: Nuclear And Fossil. A Minicourse For Secondary Schools And Adult Education. Text.” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ ERIC ED099200: The Enviornmental Impact Of Electrical Power Generation: Nuclear And Fossil. A Minicourse For Secondary Schools And Adult Education. Text.
- Author: ERIC
- Language: English
“ERIC ED099200: The Enviornmental Impact Of Electrical Power Generation: Nuclear And Fossil. A Minicourse For Secondary Schools And Adult Education. Text.” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ ERIC Archive - Adult Education - Conservation Education - Economics - Energy - Environmental Education - Environmental Influences - Fuels - Instructional Materials - Interdisciplinary Approach - Natural Resources - Nuclear Energy - Pollution - Science Education - Secondary Education - McDermott, John J., Ed.
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ERIC_ED099200
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 126.41 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 327 times, the file-s went public at Tue Jun 02 2015.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Animated GIF - Archive BitTorrent - DjVu - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find ERIC ED099200: The Enviornmental Impact Of Electrical Power Generation: Nuclear And Fossil. A Minicourse For Secondary Schools And Adult Education. Text. at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
23ERIC EJ1137718: Microstructural (Cohesion And Coherence) Text Generation Problems Of Syrian Refugee Students Learning Turkish
By ERIC
In language education, teaching a language as a foreign language is an emerging field compared to teaching it as a mother tongue. However, the experiences obtained in mother tongue education are adapted to teaching a language as a foreign language with various amendments and therefore progress in this field has been achieved. Council of Europe presented some common criteria for teaching a language as a foreign language and these criteria are put into practice in many countries, including Turkey, therefore Common European Framework of Reference for Languages is also applied in teaching Turkish as a foreign language. Using a microstructural analysis, this study tries to describe the problems and/or challenges in "text writing" as a product of Turkish writing act process experienced by Syrian refugees that were forced to take refuge in Turkey due to various reasons.
“ERIC EJ1137718: Microstructural (Cohesion And Coherence) Text Generation Problems Of Syrian Refugee Students Learning Turkish” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ ERIC EJ1137718: Microstructural (Cohesion And Coherence) Text Generation Problems Of Syrian Refugee Students Learning Turkish
- Author: ERIC
- Language: English
“ERIC EJ1137718: Microstructural (Cohesion And Coherence) Text Generation Problems Of Syrian Refugee Students Learning Turkish” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ ERIC Archive - Refugees - Second Language Learning - Second Language Instruction - Turkish - Foreign Countries - Teaching Methods - Guidelines - Writing Processes - Writing Difficulties - Connected Discourse - Writing Instruction - Writing Skills - College Students - Writing Evaluation - Measurement Techniques - Universities - Demirgünes, Sercan
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ERIC_EJ1137718
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 9.56 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 53 times, the file-s went public at Fri Oct 19 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find ERIC EJ1137718: Microstructural (Cohesion And Coherence) Text Generation Problems Of Syrian Refugee Students Learning Turkish at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
24Microsoft Research Audio 104302: Enhancing Text Representation Through Knowledge-Based Feature Generation
By Microsoft Research
Imagine an automatic news filtering system that tracks company news. Given the news item 'FDA approves ciprofloxacin for victims of anthrax inhalation', how can the system know that the drug mentioned is an antibiotic produced by Bayer? Or consider an information professional searching for data on RFID technology - how can a computer understand that the item 'Wal-Mart supply chain goes real time' is relevant for the search? Algorithms we present can do just that. When humans approach text processing tasks, such as text categorization, they interpret documents in the context of their background knowledge and experience. On the other hand, conventional information retrieval systems represent documents as bags of words, and are restricted to learning from individual word occurrences in the (necessarily limited) training set. We propose to enrich document representation through automatic use of vast repositories of human knowledge. To this end, we use knowledge concepts derived from the Open Directory Project and Wikipedia, the largest Web directory and encyclopedia, respectively. In the preprocessing phase, a feature generator analyzes the input documents and maps them onto relevant concepts. The latter give rise to a set of generated features that augment the standard bag of words. Feature generation is accomplished through contextual analysis of document text, thus implicitly performing word sense disambiguation. Coupled with the ability to generalize from words to concepts, this approach addresses the two main problems of natural language processing synonymy and polysemy. Categorizing documents with the aid of knowledge-based features leverages information that cannot be deduced from the training documents alone. Empirical results confirm that this knowledge-intensive representation brings text categorization to a qualitatively new level of performance across a diverse collection of datasets. We also propose a new, knowledge-based approach for computing the degree of semantic relatedness of texts. ©2006 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
“Microsoft Research Audio 104302: Enhancing Text Representation Through Knowledge-Based Feature Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Microsoft Research Audio 104302: Enhancing Text Representation Through Knowledge-Based Feature Generation
- Author: Microsoft Research
- Language: English
“Microsoft Research Audio 104302: Enhancing Text Representation Through Knowledge-Based Feature Generation” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ Microsoft Research - Microsoft Research Audio MP3 Archive - Paul Viola - Evgeniy Gabrilovich
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ➤ Microsoft_Research_Audio_104302
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "audio" format, the size of the file-s is: 61.18 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 6 times, the file-s went public at Sat Nov 23 2013.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - Metadata - Ogg Vorbis - PNG - VBR MP3 -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Microsoft Research Audio 104302: Enhancing Text Representation Through Knowledge-Based Feature Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
25Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - Senator Tim Scott: President Trump’s Once-in-a-generation Tax Reform Bill That Lowered Taxes For Single Moms, Working Families And Those In Need #RNC2020
By Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
Senator Tim Scott: President Trump’s once-in-a-generation tax reform bill that lowered taxes for single moms, working families and those in need #RNC2020 https://t.co/eKl4NLcnyu Source: https://twitter.com/TeamTrump/status/1298093246929936386 Uploader: Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
“Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - Senator Tim Scott: President Trump’s Once-in-a-generation Tax Reform Bill That Lowered Taxes For Single Moms, Working Families And Those In Need #RNC2020” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - Senator Tim Scott: President Trump’s Once-in-a-generation Tax Reform Bill That Lowered Taxes For Single Moms, Working Families And Those In Need #RNC2020
- Author: ➤ Team Trump (Text VOTE to 88022)
“Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - Senator Tim Scott: President Trump’s Once-in-a-generation Tax Reform Bill That Lowered Taxes For Single Moms, Working Families And Those In Need #RNC2020” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: twitter-1298093246929936386
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "movies" format, the size of the file-s is: 2.55 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 15 times, the file-s went public at Wed Nov 04 2020.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - JPEG - JPEG Thumb - JSON - MPEG4 - Metadata - Thumbnail - Unknown -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Team Trump (Text VOTE To 88022) - Senator Tim Scott: President Trump’s Once-in-a-generation Tax Reform Bill That Lowered Taxes For Single Moms, Working Families And Those In Need #RNC2020 at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
26DTIC ADA140278: Discourse Structures For Text Generation.
By Defense Technical Information Center
Text generation programs need to be designed around a theory of text organization. This paper introduces Rhetorical Structure Theory, a theory of text structure in which each region of text has a central nuclear part and a number of satellites related to it. A natural text is analyzed as an example, the mechanisms of the theory are identified, and their formalization is discussed. In a comparison, Rhetorical Structure Theory is found to be more comprehensive and more informative about text function than the text organization parts of previous text generation systems. (Author)
“DTIC ADA140278: Discourse Structures For Text Generation.” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA140278: Discourse Structures For Text Generation.
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA140278: Discourse Structures For Text Generation.” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Mann,W C - UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA MARINA DEL REY INFORMATION SCIENCES INST - *Artificial intelligence - Computational linguistics - Natural language - Information processing - Structural analysis - Management planning and control - Problem solving - Decision making - Computer logic
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA140278
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 13.26 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 80 times, the file-s went public at Thu Jan 18 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA140278: Discourse Structures For Text Generation. at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
27Conciseness Through Aggregation In Text Generation
By James Shaw
Aggregating different pieces of similar information is necessary to generate concise and easy to understand reports in technical domains. This paper presents a general algorithm that combines similar messages in order to generate one or more coherent sentences for them. The process is not as trivial as might be expected. Problems encountered are briefly described.
“Conciseness Through Aggregation In Text Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Conciseness Through Aggregation In Text Generation
- Author: James Shaw
- Language: English
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-cmp-lg9505008
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 2.78 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 63 times, the file-s went public at Sun Sep 22 2013.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Animated GIF - Archive BitTorrent - DjVu - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Conciseness Through Aggregation In Text Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
28Neural Text Generation From Structured Data With Application To The Biography Domain
By Remi Lebret, David Grangier and Michael Auli
This paper introduces a neural model for concept-to-text generation that scales to large, rich domains. We experiment with a new dataset of biographies from Wikipedia that is an order of magnitude larger than existing resources with over 700k samples. The dataset is also vastly more diverse with a 400k vocabulary, compared to a few hundred words for Weathergov or Robocup. Our model builds upon recent work on conditional neural language model for text generation. To deal with the large vocabulary, we extend these models to mix a fixed vocabulary with copy actions that transfer sample-specific words from the input database to the generated output sentence. Our neural model significantly out-performs a classical Kneser-Ney language model adapted to this task by nearly 15 BLEU.
“Neural Text Generation From Structured Data With Application To The Biography Domain” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Neural Text Generation From Structured Data With Application To The Biography Domain
- Authors: Remi LebretDavid GrangierMichael Auli
“Neural Text Generation From Structured Data With Application To The Biography Domain” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-1603.07771
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 0.41 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 20 times, the file-s went public at Fri Jun 29 2018.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Metadata - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Neural Text Generation From Structured Data With Application To The Biography Domain at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
29Harnessing The Expertise Of 70,000 Human Editors: Knowledge-Based Feature Generation For Text Categorization
By Evgeniy Gabrilovich and Shaul Markovitch
This paper introduces a neural model for concept-to-text generation that scales to large, rich domains. We experiment with a new dataset of biographies from Wikipedia that is an order of magnitude larger than existing resources with over 700k samples. The dataset is also vastly more diverse with a 400k vocabulary, compared to a few hundred words for Weathergov or Robocup. Our model builds upon recent work on conditional neural language model for text generation. To deal with the large vocabulary, we extend these models to mix a fixed vocabulary with copy actions that transfer sample-specific words from the input database to the generated output sentence. Our neural model significantly out-performs a classical Kneser-Ney language model adapted to this task by nearly 15 BLEU.
“Harnessing The Expertise Of 70,000 Human Editors: Knowledge-Based Feature Generation For Text Categorization” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Harnessing The Expertise Of 70,000 Human Editors: Knowledge-Based Feature Generation For Text Categorization
- Authors: Evgeniy GabrilovichShaul Markovitch
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ➤ academictorrents_077b92ed26aeecc050c4f268c066563c62e405ce
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 37.04 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 64 times, the file-s went public at Tue Aug 11 2020.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - BitTorrent - BitTorrentContents - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - Unknown - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Harnessing The Expertise Of 70,000 Human Editors: Knowledge-Based Feature Generation For Text Categorization at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
30ERIC ED289476: Text Generation: The Problem Of Text Structure.
By ERIC
One of the major problems in artificial intelligence (AI) text generation is text organization; a poorly organized text can be unreadable or even misleading. A comparison of two AI approaches to text organization--McKeown's TEXT system and Rhetorical Structure Theory (RST)--shows that, although they share many assumptions about the nature of text, they are also in strong contrast. TEXT identifies text organization with whole-text nonrecursive structures, while RST uses small recursive ones. RST has an elaborate apparatus of relations between parts of texts, and of the "nuclearity" of particular parts; TEXT has no correlates for these. RST works with a wide range of relation types, TEXT with just one. TEXT is an implemented system, whereas RST is developmental. More important, TEXT develops text organizations so that they resemble patterns extracted from previous text, while RST strives for an organization which is justifiable as meeting the goals of the text being generated. This contrast raises many of the key issues in current research on the nature of text organization and how it can be created by programs. A 13-item reference list is appended. (Author/RP)
“ERIC ED289476: Text Generation: The Problem Of Text Structure.” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ ERIC ED289476: Text Generation: The Problem Of Text Structure.
- Author: ERIC
- Language: English
“ERIC ED289476: Text Generation: The Problem Of Text Structure.” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ERIC Archive - Artificial Intelligence - Comparative Analysis - Computational Linguistics - Discourse Analysis
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ERIC_ED289476
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 22.17 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 119 times, the file-s went public at Fri Dec 26 2014.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Animated GIF - Archive BitTorrent - DjVu - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find ERIC ED289476: Text Generation: The Problem Of Text Structure. at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
31Text To 3D Scene Generation With Rich Lexical Grounding
By Angel Chang, Will Monroe, Manolis Savva, Christopher Potts and Christopher D. Manning
The ability to map descriptions of scenes to 3D geometric representations has many applications in areas such as art, education, and robotics. However, prior work on the text to 3D scene generation task has used manually specified object categories and language that identifies them. We introduce a dataset of 3D scenes annotated with natural language descriptions and learn from this data how to ground textual descriptions to physical objects. Our method successfully grounds a variety of lexical terms to concrete referents, and we show quantitatively that our method improves 3D scene generation over previous work using purely rule-based methods. We evaluate the fidelity and plausibility of 3D scenes generated with our grounding approach through human judgments. To ease evaluation on this task, we also introduce an automated metric that strongly correlates with human judgments.
“Text To 3D Scene Generation With Rich Lexical Grounding” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Text To 3D Scene Generation With Rich Lexical Grounding
- Authors: Angel ChangWill MonroeManolis SavvaChristopher PottsChristopher D. Manning
- Language: English
“Text To 3D Scene Generation With Rich Lexical Grounding” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: Computation and Language - Computing Research Repository - Graphics
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-1505.06289
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 21.20 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 47 times, the file-s went public at Wed Jun 27 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - JPEG Thumb - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Text To 3D Scene Generation With Rich Lexical Grounding at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
32Affect-LM: A Neural Language Model For Customizable Affective Text Generation
By Sayan Ghosh, Mathieu Chollet, Eugene Laksana, Louis-Philippe Morency and Stefan Scherer
Human verbal communication includes affective messages which are conveyed through use of emotionally colored words. There has been a lot of research in this direction but the problem of integrating state-of-the-art neural language models with affective information remains an area ripe for exploration. In this paper, we propose an extension to an LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) language model for generating conversational text, conditioned on affect categories. Our proposed model, Affect-LM enables us to customize the degree of emotional content in generated sentences through an additional design parameter. Perception studies conducted using Amazon Mechanical Turk show that Affect-LM generates naturally looking emotional sentences without sacrificing grammatical correctness. Affect-LM also learns affect-discriminative word representations, and perplexity experiments show that additional affective information in conversational text can improve language model prediction.
“Affect-LM: A Neural Language Model For Customizable Affective Text Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Affect-LM: A Neural Language Model For Customizable Affective Text Generation
- Authors: Sayan GhoshMathieu CholletEugene LaksanaLouis-Philippe MorencyStefan Scherer
“Affect-LM: A Neural Language Model For Customizable Affective Text Generation” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-1704.06851
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 0.68 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 32 times, the file-s went public at Sat Jun 30 2018.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Metadata - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Affect-LM: A Neural Language Model For Customizable Affective Text Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
33AMR-to-text Generation As A Traveling Salesman Problem
By Linfeng Song, Yue Zhang, Xiaochang Peng, Zhiguo Wang and Daniel Gildea
The task of AMR-to-text generation is to generate grammatical text that sustains the semantic meaning for a given AMR graph. We at- tack the task by first partitioning the AMR graph into smaller fragments, and then generating the translation for each fragment, before finally deciding the order by solving an asymmetric generalized traveling salesman problem (AGTSP). A Maximum Entropy classifier is trained to estimate the traveling costs, and a TSP solver is used to find the optimized solution. The final model reports a BLEU score of 22.44 on the SemEval-2016 Task8 dataset.
“AMR-to-text Generation As A Traveling Salesman Problem” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ AMR-to-text Generation As A Traveling Salesman Problem
- Authors: Linfeng SongYue ZhangXiaochang PengZhiguo WangDaniel Gildea
“AMR-to-text Generation As A Traveling Salesman Problem” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-1609.07451
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 0.19 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 31 times, the file-s went public at Fri Jun 29 2018.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Metadata - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find AMR-to-text Generation As A Traveling Salesman Problem at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
34Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_03-07-18
By oobabooga
A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Supports transformers, GPTQ, llama.cpp (ggml/gguf), Llama models. Text generation web UI A Gradio web UI for Large Language Models. Its goal is to become the AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webui of text generation. | | ||:---:|:---:|| | | Features 3 interface modes: default (two columns), notebook, and chat Multiple model backends: transformers , llama.cpp , ExLlama , AutoGPTQ , GPTQ-for-LLaMa , ctransformers Dropdown menu for quickly switching between different models LoRA: load and unload LoRAs on the fly, train a new LoRA using QLoRA Precise instruction templates for chat mode, including Llama-2-chat, Alpaca, Vicuna, WizardLM, StableLM, and many others 4-bit, 8-bit, and CPU inference through the transformers library Use llama.cpp models with transformers samplers ( llamacpp_HF loader) Multimodal pipelines, including LLaVA and MiniGPT-4 Extensions framework Custom chat characters Very efficient text streaming Markdown output with LaTeX rendering, to use for instance with GALACTICA API, including endpoints for websocket streaming ( see the examples ) To learn how to use the various features, check out the Documentation: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui/tree/main/docs Installation One-click installers | Windows | Linux | macOS | WSL ||--------|--------|--------|--------|| oobabooga-windows.zip | oobabooga-linux.zip | oobabooga-macos.zip | oobabooga-wsl.zip | Just download the zip above, extract it, and double-click on "start". The web UI and all its dependencies will be installed in the same folder. The source codes and more information can be found here: https://github.com/oobabooga/one-click-installers There is no need to run the installers as admin. Huge thanks to @jllllll , @ClayShoaf , and @xNul for their contributions to these installers. Manual installation using Conda Recommended if you have some experience with the command-line. 0. Install Conda https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html On Linux or WSL, it can be automatically installed with these two commands ( source ): curl -sL "https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh" > "Miniconda3.sh"bash Miniconda3.sh 1. Create a new conda environment conda create -n textgen python=3.10.9conda activate textgen 2. Install Pytorch | System | GPU | Command ||--------|---------|---------|| Linux/WSL | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Linux/WSL | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu || Linux | AMD | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm5.4.2 || MacOS + MPS | Any | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio || Windows | NVIDIA | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu117 || Windows | CPU only | pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio | The up-to-date commands can be found here: https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/. 2.1 Additional information MacOS users: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui/pull/393 AMD users: https://rentry.org/eq3hg 3. Install the web UI git clone https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webuicd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt llama.cpp on AMD, Metal, and some specific CPUs Precompiled wheels are included for CPU-only and NVIDIA GPUs (cuBLAS). For AMD, Metal, and some specific CPUs, you need to uninstall those wheels and compile llama-cpp-python yourself. To uninstall: pip uninstall -y llama-cpp-python llama-cpp-python-cuda To compile: https://github.com/abetlen/llama-cpp-python#installation-with-openblas--cublas--clblast--metal bitsandbytes on older NVIDIA GPUs bitsandbytes >= 0.39 may not work. In that case, to use --load-in-8bit , you may have to downgrade like this: Linux: pip install bitsandbytes==0.38.1 Windows: pip install https://github.com/jllllll/bitsandbytes-windows-webui/raw/main/bitsandbytes-0.38.1-py3-none-any.whl Alternative: Docker ```ln -s docker/{Dockerfile,docker-compose.yml,.dockerignore} .cp docker/.env.example .env Edit .env and set TORCH CUDA ARCH_LIST based on your GPU model docker compose up --build``` You need to have docker compose v2.17 or higher installed. See this guide for instructions. For additional docker files, check out this repository . Updating the requirements From time to time, the requirements.txt changes. To update, use these commands: conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipip install -r requirements.txt --upgrade Downloading models Models should be placed in the text-generation-webui/models folder. They are usually downloaded from Hugging Face . Transformers or GPTQ models are made of several files and must be placed in a subfolder. Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── lmsys_vicuna-33b-v1.3│ │ ├── config.json│ │ ├── generation_config.json│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00001-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00002-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00003-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00004-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00005-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00006-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model-00007-of-00007.bin│ │ ├── pytorch_model.bin.index.json│ │ ├── special_tokens_map.json│ │ ├── tokenizer_config.json│ │ └── tokenizer.model In the "Model" tab of the UI, those models can be automatically downloaded from Hugging Face. You can also download them via the command-line with python download-model.py organization/model . GGML/GGUF models are a single file and should be placed directly into models . Example: text-generation-webui├── models│ ├── llama-13b.ggmlv3.q4_K_M.bin GPT-4chan Instructions GPT-4chan has been shut down from Hugging Face, so you need to download it elsewhere. You have two options: Torrent: 16-bit / 32-bit Direct download: 16-bit / 32-bit The 32-bit version is only relevant if you intend to run the model in CPU mode. Otherwise, you should use the 16-bit version. After downloading the model, follow these steps: Place the files under models/gpt4chan_model_float16 or models/gpt4chan_model . Place GPT-J 6B's config.json file in that same folder: config.json . Download GPT-J 6B's tokenizer files (they will be automatically detected when you attempt to load GPT-4chan): python download-model.py EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B --text-only When you load this model in default or notebook modes, the "HTML" tab will show the generated text in 4chan format: Starting the web UI conda activate textgencd text-generation-webuipython server.py Then browse to http://localhost:7860/?__theme=dark Optionally, you can use the following command-line flags: Basic settings | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| -h , --help | Show this help message and exit. || --multi-user | Multi-user mode. Chat histories are not saved or automatically loaded. WARNING: this is highly experimental. || --character CHARACTER | The name of the character to load in chat mode by default. || --model MODEL | Name of the model to load by default. || --lora LORA [LORA ...] | The list of LoRAs to load. If you want to load more than one LoRA, write the names separated by spaces. || --model-dir MODEL_DIR | Path to directory with all the models. || --lora-dir LORA_DIR | Path to directory with all the loras. || --model-menu | Show a model menu in the terminal when the web UI is first launched. || --settings SETTINGS_FILE | Load the default interface settings from this yaml file. See settings-template.yaml for an example. If you create a file called settings.yaml , this file will be loaded by default without the need to use the --settings flag. || --extensions EXTENSIONS [EXTENSIONS ...] | The list of extensions to load. If you want to load more than one extension, write the names separated by spaces. || --verbose | Print the prompts to the terminal. | Model loader | Flag | Description ||--------------------------------------------|-------------|| --loader LOADER | Choose the model loader manually, otherwise, it will get autodetected. Valid options: transformers, autogptq, gptq-for-llama, exllama, exllama_hf, llamacpp, rwkv, ctransformers | Accelerate/transformers | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --cpu | Use the CPU to generate text. Warning: Training on CPU is extremely slow.|| --auto-devices | Automatically split the model across the available GPU(s) and CPU. || --gpu-memory GPU_MEMORY [GPU_MEMORY ...] | Maximum GPU memory in GiB to be allocated per GPU. Example: --gpu-memory 10 for a single GPU, --gpu-memory 10 5 for two GPUs. You can also set values in MiB like --gpu-memory 3500MiB . || --cpu-memory CPU_MEMORY | Maximum CPU memory in GiB to allocate for offloaded weights. Same as above.|| --disk | If the model is too large for your GPU(s) and CPU combined, send the remaining layers to the disk. || --disk-cache-dir DISK_CACHE_DIR | Directory to save the disk cache to. Defaults to cache/ . || --load-in-8bit | Load the model with 8-bit precision (using bitsandbytes).|| --bf16 | Load the model with bfloat16 precision. Requires NVIDIA Ampere GPU. || --no-cache | Set use_cache to False while generating text. This reduces the VRAM usage a bit with a performance cost. || --xformers | Use xformer's memory efficient attention. This should increase your tokens/s. || --sdp-attention | Use torch 2.0's sdp attention. || --trust-remote-code | Set trust remote code=True while loading a model. Necessary for ChatGLM and Falcon. | Accelerate 4-bit ⚠️ Requires minimum compute of 7.0 on Windows at the moment. | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------------|-------------|| --load-in-4bit | Load the model with 4-bit precision (using bitsandbytes). || --compute_dtype COMPUTE_DTYPE | compute dtype for 4-bit. Valid options: bfloat16, float16, float32. || --quant_type QUANT_TYPE | quant type for 4-bit. Valid options: nf4, fp4. || --use_double_quant | use double_quant for 4-bit. | GGML/GGUF (for llama.cpp and ctransformers) | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --threads | Number of threads to use. || --n_batch | Maximum number of prompt tokens to batch together when calling llama_eval. || --n-gpu-layers N_GPU_LAYERS | Number of layers to offload to the GPU. Only works if llama-cpp-python was compiled with BLAS. Set this to 1000000000 to offload all layers to the GPU. || --n_ctx N_CTX | Size of the prompt context. | llama.cpp | Flag | Description ||---------------|---------------|| --no-mmap | Prevent mmap from being used. || --mlock | Force the system to keep the model in RAM. || --mul_mat_q | Activate new mulmat kernels. || --cache-capacity CACHE_CAPACITY | Maximum cache capacity. Examples: 2000MiB, 2GiB. When provided without units, bytes will be assumed. || --tensor_split TENSOR_SPLIT | Split the model across multiple GPUs, comma-separated list of proportions, e.g. 18,17 || --llama_cpp_seed SEED | Seed for llama-cpp models. Default 0 (random). || --n_gqa N_GQA | GGML only (not used by GGUF): Grouped-Query Attention. Must be 8 for llama-2 70b. || --rms_norm_eps RMS_NORM_EPS | GGML only (not used by GGUF): 5e-6 is a good value for llama-2 models. || --cpu | Use the CPU version of llama-cpp-python instead of the GPU-accelerated version. || --cfg-cache | llamacpp_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. | ctransformers | Flag | Description ||-------------|-------------|| --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently gpt2, gptj, gptneox, falcon, llama, mpt, starcoder (gptbigcode), dollyv2, and replit are supported. | AutoGPTQ | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --triton | Use triton. || --no_inject_fused_attention | Disable the use of fused attention, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_inject_fused_mlp | Triton mode only: disable the use of fused MLP, which will use less VRAM at the cost of slower inference. || --no_use_cuda_fp16 | This can make models faster on some systems. || --desc_act | For models that don't have a quantize config.json, this parameter is used to define whether to set desc act or not in BaseQuantizeConfig. || --disable_exllama | Disable ExLlama kernel, which can improve inference speed on some systems. | ExLlama | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --gpu-split | Comma-separated list of VRAM (in GB) to use per GPU device for model layers, e.g. 20,7,7 || --max_seq_len MAX_SEQ_LEN | Maximum sequence length. || --cfg-cache | ExLlama_HF: Create an additional cache for CFG negative prompts. Necessary to use CFG with that loader, but not necessary for CFG with base ExLlama. | GPTQ-for-LLaMa | Flag | Description ||---------------------------|-------------|| --wbits WBITS | Load a pre-quantized model with specified precision in bits. 2, 3, 4 and 8 are supported. || --model_type MODEL_TYPE | Model type of pre-quantized model. Currently LLaMA, OPT, and GPT-J are supported. || --groupsize GROUPSIZE | Group size. || --pre_layer PRE_LAYER [PRE_LAYER ...] | The number of layers to allocate to the GPU. Setting this parameter enables CPU offloading for 4-bit models. For multi-gpu, write the numbers separated by spaces, eg --pre_layer 30 60 . || --checkpoint CHECKPOINT | The path to the quantized checkpoint file. If not specified, it will be automatically detected. || --monkey-patch | Apply the monkey patch for using LoRAs with quantized models. DeepSpeed | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --deepspeed | Enable the use of DeepSpeed ZeRO-3 for inference via the Transformers integration. || --nvme-offload-dir NVME_OFFLOAD_DIR | DeepSpeed: Directory to use for ZeRO-3 NVME offloading. || --local_rank LOCAL_RANK | DeepSpeed: Optional argument for distributed setups. | RWKV | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------|-------------|| --rwkv-strategy RWKV_STRATEGY | RWKV: The strategy to use while loading the model. Examples: "cpu fp32", "cuda fp16", "cuda fp16i8". || --rwkv-cuda-on | RWKV: Compile the CUDA kernel for better performance. | RoPE (for llama.cpp, ExLlama, and transformers) | Flag | Description ||------------------|-------------|| --alpha_value ALPHA_VALUE | Positional embeddings alpha factor for NTK RoPE scaling. Use either this or compress pos emb, not both. || --rope_freq_base ROPE_FREQ_BASE | If greater than 0, will be used instead of alpha value. Those two are related by rope freq base = 10000 * alpha value ^ (64 / 63). || --compress_pos_emb COMPRESS_POS_EMB | Positional embeddings compression factor. Should be set to (context length) / (model's original context length). Equal to 1/rope freq scale. | Gradio | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --listen | Make the web UI reachable from your local network. || --listen-host LISTEN_HOST | The hostname that the server will use. || --listen-port LISTEN_PORT | The listening port that the server will use. || --share | Create a public URL. This is useful for running the web UI on Google Colab or similar. || --auto-launch | Open the web UI in the default browser upon launch. || --gradio-auth USER:PWD | set gradio authentication like "username:password"; or comma-delimit multiple like "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --gradio-auth-path GRADIO_AUTH_PATH | Set the gradio authentication file path. The file should contain one or more user:password pairs in this format: "u1:p1,u2:p2,u3:p3" || --ssl-keyfile SSL_KEYFILE | The path to the SSL certificate key file. || --ssl-certfile SSL_CERTFILE | The path to the SSL certificate cert file. | API | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --api | Enable the API extension. || --public-api | Create a public URL for the API using Cloudfare. || --public-api-id PUBLIC_API_ID | Tunnel ID for named Cloudflare Tunnel. Use together with public-api option. || --api-blocking-port BLOCKING_PORT | The listening port for the blocking API. || --api-streaming-port STREAMING_PORT | The listening port for the streaming API. | Multimodal | Flag | Description ||---------------------------------------|-------------|| --multimodal-pipeline PIPELINE | The multimodal pipeline to use. Examples: llava-7b , llava-13b . | Presets Inference settings presets can be created under presets/ as yaml files. These files are detected automatically at startup. The presets that are included by default are the result of a contest that received 7215 votes. More details can be found here . Contributing If you would like to contribute to the project, check out the Contributing guidelines . Community Subreddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/oobabooga/ Discord: https://discord.gg/jwZCF2dPQN Acknowledgment In August 2023, Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) provided a generous grant to encourage and support my independent work on this project. I am extremely grateful for their trust and recognition, which will allow me to dedicate more time towards realizing the full potential of text-generation-webui. To restore the repository download the bundle wget https://archive.org/download/github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_03-07-18/oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_03-07-18.bundle and run: git clone oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_03-07-18.bundle Source: https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui Uploader: oobabooga Upload date: 2023-08-30
“Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_03-07-18” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_03-07-18
- Author: oobabooga
“Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_03-07-18” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ➤ github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_03-07-18
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "software" format, the size of the file-s is: 3.94 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 439 times, the file-s went public at Wed Aug 30 2023.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - JPEG - JPEG Thumb - Metadata - Unknown -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Github.com-oobabooga-text-generation-webui_-_2023-08-30_03-07-18 at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
35Github.com-huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42
By huggingface
Large Language Model Text Generation Inference 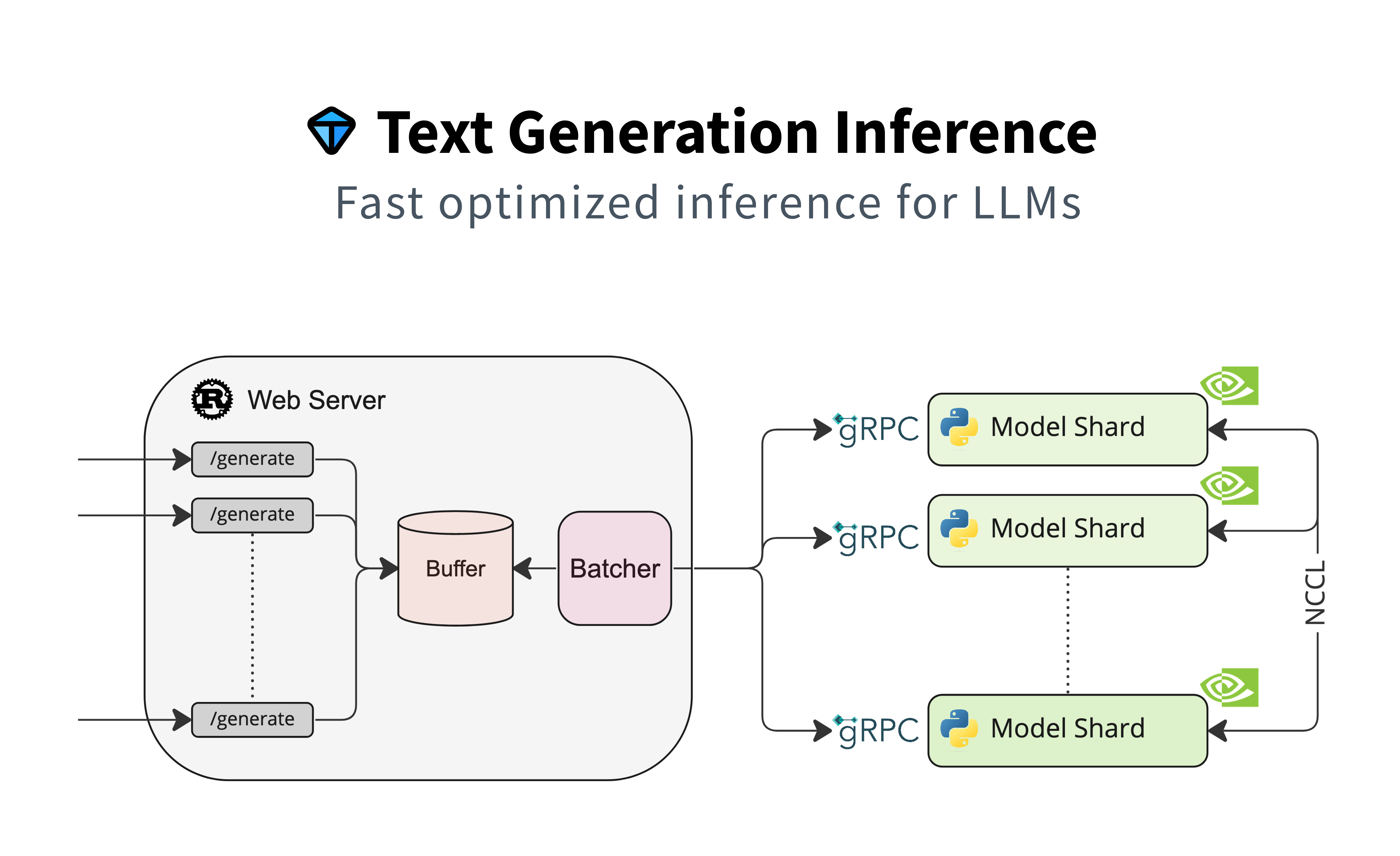# Text Generation Inference A Rust, Python and gRPC server for text generation inference. Used in production at [HuggingFace](https://huggingface.co)to power Hugging Chat, the Inference API and Inference Endpoint. Table of contents Features Optimized Architectures Get Started Docker API Documentation Using a private or gated model A note on Shared Memory Distributed Tracing Local Install CUDA Kernels Run Falcon Run Quantization Develop Testing Other supported hardware Features Serve the most popular Large Language Models with a simple launcher Tensor Parallelism for faster inference on multiple GPUs Token streaming using Server-Sent Events (SSE) Continuous batching of incoming requests for increased total throughput Optimized transformers code for inference using flash-attention and Paged Attention on the most popular architectures Quantization with bitsandbytes and GPT-Q Safetensors weight loading Watermarking with A Watermark for Large Language Models Logits warper (temperature scaling, top-p, top-k, repetition penalty, more details see transformers.LogitsProcessor ) Stop sequences Log probabilities Production ready (distributed tracing with Open Telemetry, Prometheus metrics) Optimized architectures BLOOM FLAN-T5 Galactica GPT-Neox Llama OPT SantaCoder Starcoder Falcon 7B Falcon 40B MPT Llama V2 Other architectures are supported on a best effort basis using: AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto") or AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto") Get started Docker The easiest way of getting started is using the official Docker container: ```shellmodel=tiiuae/falcon-7b-instructvolume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every run docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.0 --model-id $model``` Note: To use GPUs, you need to install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit . We also recommend using NVIDIA drivers with CUDA version 11.8 or higher. To see all options to serve your models (in the code or in the cli: text-generation-launcher --help You can then query the model using either the /generate or /generate_stream routes: shellcurl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate \ -X POST \ -d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' shellcurl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate_stream \ -X POST \ -d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' or from Python: shellpip install text-generation ```pythonfrom text_generation import Client client = Client("http://127.0.0.1:8080")print(client.generate("What is Deep Learning?", max new tokens=20).generated_text) text = ""for response in client.generate stream("What is Deep Learning?", max new_tokens=20): if not response.token.special: text += response.token.textprint(text)``` API documentation You can consult the OpenAPI documentation of the text-generation-inference REST API using the /docs route.The Swagger UI is also available at: https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference . Using a private or gated model You have the option to utilize the HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN environment variable for configuring the token employed by text-generation-inference . This allows you to gain access to protected resources. For example, if you want to serve the gated Llama V2 model variants: Go to https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens Copy your cli READ token Export HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=<your cli READ token> or with Docker: ```shellmodel=meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hfvolume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every runtoken= docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -e HUGGING FACE HUB_TOKEN=$token -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.0 --model-id $model``` A note on Shared Memory (shm) <code>NCCL</code> is a communication framework used by PyTorch to do distributed training/inference. text-generation-inference makeuse of NCCL to enable Tensor Parallelism to dramatically speed up inference for large language models. In order to share data between the different devices of a NCCL group, NCCL might fall back to using the host memory ifpeer-to-peer using NVLink or PCI is not possible. To allow the container to use 1G of Shared Memory and support SHM sharing, we add --shm-size 1g on the above command. If you are running text-generation-inference inside Kubernetes . You can also add Shared Memory to the container bycreating a volume with: yaml- name: shm emptyDir: medium: Memory sizeLimit: 1Gi and mounting it to /dev/shm . Finally, you can also disable SHM sharing by using the NCCL_SHM_DISABLE=1 environment variable. However, note thatthis will impact performance. Distributed Tracing text-generation-inference is instrumented with distributed tracing using OpenTelemetry. You can use this featureby setting the address to an OTLP collector with the --otlp-endpoint argument. Local install You can also opt to install text-generation-inference locally. First install Rust and create a Python virtual environment with at leastPython 3.9, e.g. using conda : ```shellcurl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh conda create -n text-generation-inference python=3.9conda activate text-generation-inference``` You may also need to install Protoc. On Linux: shellPROTOC_ZIP=protoc-21.12-linux-x86_64.zipcurl -OL https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.12/$PROTOC_ZIPsudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local bin/protocsudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local 'include/*'rm -f $PROTOC_ZIP On MacOS, using Homebrew: shellbrew install protobuf Then run: shellBUILD_EXTENSIONS=True make install # Install repository and HF/transformer fork with CUDA kernelsmake run-falcon-7b-instruct Note: on some machines, you may also need the OpenSSL libraries and gcc. On Linux machines, run: shellsudo apt-get install libssl-dev gcc -y CUDA Kernels The custom CUDA kernels are only tested on NVIDIA A100s. If you have any installation or runtime issues, you can removethe kernels by using the DISABLE_CUSTOM_KERNELS=True environment variable. Be aware that the official Docker image has them enabled by default. Run Falcon Run shellmake run-falcon-7b-instruct Quantization You can also quantize the weights with bitsandbytes to reduce the VRAM requirement: shellmake run-falcon-7b-instruct-quantize Develop shellmake server-devmake router-dev Testing ```shell python make python-server-testsmake python-client-tests or both server and client tests make python-tests rust cargo tests make rust-tests integration tests make integration-tests``` Other supported hardware TGI is also supported on the following AI hardware accelerators:- Habana first-gen Gaudi and Gaudi2: checkout here how to serve models with TGI on Gaudi and Gaudi2 with Optimum Habana To restore the repository download the bundle wget https://archive.org/download/github.com-huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42/huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42.bundle and run: git clone huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42.bundle Source: https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference Uploader: huggingface Upload date: 2023-08-01
“Github.com-huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Github.com-huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42
- Author: huggingface
“Github.com-huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ➤ github.com-huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "software" format, the size of the file-s is: 2.38 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 31 times, the file-s went public at Tue Aug 01 2023.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - JPEG - JPEG Thumb - Metadata - Unknown -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Github.com-huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42 at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
36Segregatory Coordination And Ellipsis In Text Generation
Large Language Model Text Generation Inference # Text Generation Inference A Rust, Python and gRPC server for text generation inference. Used in production at [HuggingFace](https://huggingface.co)to power Hugging Chat, the Inference API and Inference Endpoint. Table of contents Features Optimized Architectures Get Started Docker API Documentation Using a private or gated model A note on Shared Memory Distributed Tracing Local Install CUDA Kernels Run Falcon Run Quantization Develop Testing Other supported hardware Features Serve the most popular Large Language Models with a simple launcher Tensor Parallelism for faster inference on multiple GPUs Token streaming using Server-Sent Events (SSE) Continuous batching of incoming requests for increased total throughput Optimized transformers code for inference using flash-attention and Paged Attention on the most popular architectures Quantization with bitsandbytes and GPT-Q Safetensors weight loading Watermarking with A Watermark for Large Language Models Logits warper (temperature scaling, top-p, top-k, repetition penalty, more details see transformers.LogitsProcessor ) Stop sequences Log probabilities Production ready (distributed tracing with Open Telemetry, Prometheus metrics) Optimized architectures BLOOM FLAN-T5 Galactica GPT-Neox Llama OPT SantaCoder Starcoder Falcon 7B Falcon 40B MPT Llama V2 Other architectures are supported on a best effort basis using: AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto") or AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto") Get started Docker The easiest way of getting started is using the official Docker container: ```shellmodel=tiiuae/falcon-7b-instructvolume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every run docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.0 --model-id $model``` Note: To use GPUs, you need to install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit . We also recommend using NVIDIA drivers with CUDA version 11.8 or higher. To see all options to serve your models (in the code or in the cli: text-generation-launcher --help You can then query the model using either the /generate or /generate_stream routes: shellcurl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate \ -X POST \ -d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' shellcurl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate_stream \ -X POST \ -d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' or from Python: shellpip install text-generation ```pythonfrom text_generation import Client client = Client("http://127.0.0.1:8080")print(client.generate("What is Deep Learning?", max new tokens=20).generated_text) text = ""for response in client.generate stream("What is Deep Learning?", max new_tokens=20): if not response.token.special: text += response.token.textprint(text)``` API documentation You can consult the OpenAPI documentation of the text-generation-inference REST API using the /docs route.The Swagger UI is also available at: https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference . Using a private or gated model You have the option to utilize the HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN environment variable for configuring the token employed by text-generation-inference . This allows you to gain access to protected resources. For example, if you want to serve the gated Llama V2 model variants: Go to https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens Copy your cli READ token Export HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=<your cli READ token> or with Docker: ```shellmodel=meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hfvolume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every runtoken= docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -e HUGGING FACE HUB_TOKEN=$token -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.0 --model-id $model``` A note on Shared Memory (shm) <code>NCCL</code> is a communication framework used by PyTorch to do distributed training/inference. text-generation-inference makeuse of NCCL to enable Tensor Parallelism to dramatically speed up inference for large language models. In order to share data between the different devices of a NCCL group, NCCL might fall back to using the host memory ifpeer-to-peer using NVLink or PCI is not possible. To allow the container to use 1G of Shared Memory and support SHM sharing, we add --shm-size 1g on the above command. If you are running text-generation-inference inside Kubernetes . You can also add Shared Memory to the container bycreating a volume with: yaml- name: shm emptyDir: medium: Memory sizeLimit: 1Gi and mounting it to /dev/shm . Finally, you can also disable SHM sharing by using the NCCL_SHM_DISABLE=1 environment variable. However, note thatthis will impact performance. Distributed Tracing text-generation-inference is instrumented with distributed tracing using OpenTelemetry. You can use this featureby setting the address to an OTLP collector with the --otlp-endpoint argument. Local install You can also opt to install text-generation-inference locally. First install Rust and create a Python virtual environment with at leastPython 3.9, e.g. using conda : ```shellcurl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh conda create -n text-generation-inference python=3.9conda activate text-generation-inference``` You may also need to install Protoc. On Linux: shellPROTOC_ZIP=protoc-21.12-linux-x86_64.zipcurl -OL https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.12/$PROTOC_ZIPsudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local bin/protocsudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local 'include/*'rm -f $PROTOC_ZIP On MacOS, using Homebrew: shellbrew install protobuf Then run: shellBUILD_EXTENSIONS=True make install # Install repository and HF/transformer fork with CUDA kernelsmake run-falcon-7b-instruct Note: on some machines, you may also need the OpenSSL libraries and gcc. On Linux machines, run: shellsudo apt-get install libssl-dev gcc -y CUDA Kernels The custom CUDA kernels are only tested on NVIDIA A100s. If you have any installation or runtime issues, you can removethe kernels by using the DISABLE_CUSTOM_KERNELS=True environment variable. Be aware that the official Docker image has them enabled by default. Run Falcon Run shellmake run-falcon-7b-instruct Quantization You can also quantize the weights with bitsandbytes to reduce the VRAM requirement: shellmake run-falcon-7b-instruct-quantize Develop shellmake server-devmake router-dev Testing ```shell python make python-server-testsmake python-client-tests or both server and client tests make python-tests rust cargo tests make rust-tests integration tests make integration-tests``` Other supported hardware TGI is also supported on the following AI hardware accelerators:- Habana first-gen Gaudi and Gaudi2: checkout here how to serve models with TGI on Gaudi and Gaudi2 with Optimum Habana To restore the repository download the bundle wget https://archive.org/download/github.com-huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42/huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42.bundle and run: git clone huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42.bundle Source: https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference Uploader: huggingface Upload date: 2023-08-01
“Segregatory Coordination And Ellipsis In Text Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Segregatory Coordination And Ellipsis In Text Generation
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-cmp-lg9808016
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 6.31 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 69 times, the file-s went public at Sat Sep 21 2013.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Animated GIF - Archive BitTorrent - DjVu - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Segregatory Coordination And Ellipsis In Text Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
37Computer Mediated Communication : Computer Conferencing - Electronic Mail, Electronic Publishing - Computer Interviewing, Interactive Text Reading - Group Decision Support Systems, Idea Generation Support Systems, Human Machine Communication, Multi-media Communication, Hypertext - Hypermedia - Linguistic Games : Bibliography
By Sabourin, Conrad, 1943-
Large Language Model Text Generation Inference # Text Generation Inference A Rust, Python and gRPC server for text generation inference. Used in production at [HuggingFace](https://huggingface.co)to power Hugging Chat, the Inference API and Inference Endpoint. Table of contents Features Optimized Architectures Get Started Docker API Documentation Using a private or gated model A note on Shared Memory Distributed Tracing Local Install CUDA Kernels Run Falcon Run Quantization Develop Testing Other supported hardware Features Serve the most popular Large Language Models with a simple launcher Tensor Parallelism for faster inference on multiple GPUs Token streaming using Server-Sent Events (SSE) Continuous batching of incoming requests for increased total throughput Optimized transformers code for inference using flash-attention and Paged Attention on the most popular architectures Quantization with bitsandbytes and GPT-Q Safetensors weight loading Watermarking with A Watermark for Large Language Models Logits warper (temperature scaling, top-p, top-k, repetition penalty, more details see transformers.LogitsProcessor ) Stop sequences Log probabilities Production ready (distributed tracing with Open Telemetry, Prometheus metrics) Optimized architectures BLOOM FLAN-T5 Galactica GPT-Neox Llama OPT SantaCoder Starcoder Falcon 7B Falcon 40B MPT Llama V2 Other architectures are supported on a best effort basis using: AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto") or AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto") Get started Docker The easiest way of getting started is using the official Docker container: ```shellmodel=tiiuae/falcon-7b-instructvolume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every run docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.0 --model-id $model``` Note: To use GPUs, you need to install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit . We also recommend using NVIDIA drivers with CUDA version 11.8 or higher. To see all options to serve your models (in the code or in the cli: text-generation-launcher --help You can then query the model using either the /generate or /generate_stream routes: shellcurl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate \ -X POST \ -d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' shellcurl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate_stream \ -X POST \ -d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' or from Python: shellpip install text-generation ```pythonfrom text_generation import Client client = Client("http://127.0.0.1:8080")print(client.generate("What is Deep Learning?", max new tokens=20).generated_text) text = ""for response in client.generate stream("What is Deep Learning?", max new_tokens=20): if not response.token.special: text += response.token.textprint(text)``` API documentation You can consult the OpenAPI documentation of the text-generation-inference REST API using the /docs route.The Swagger UI is also available at: https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference . Using a private or gated model You have the option to utilize the HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN environment variable for configuring the token employed by text-generation-inference . This allows you to gain access to protected resources. For example, if you want to serve the gated Llama V2 model variants: Go to https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens Copy your cli READ token Export HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=<your cli READ token> or with Docker: ```shellmodel=meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hfvolume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every runtoken= docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -e HUGGING FACE HUB_TOKEN=$token -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.0 --model-id $model``` A note on Shared Memory (shm) <code>NCCL</code> is a communication framework used by PyTorch to do distributed training/inference. text-generation-inference makeuse of NCCL to enable Tensor Parallelism to dramatically speed up inference for large language models. In order to share data between the different devices of a NCCL group, NCCL might fall back to using the host memory ifpeer-to-peer using NVLink or PCI is not possible. To allow the container to use 1G of Shared Memory and support SHM sharing, we add --shm-size 1g on the above command. If you are running text-generation-inference inside Kubernetes . You can also add Shared Memory to the container bycreating a volume with: yaml- name: shm emptyDir: medium: Memory sizeLimit: 1Gi and mounting it to /dev/shm . Finally, you can also disable SHM sharing by using the NCCL_SHM_DISABLE=1 environment variable. However, note thatthis will impact performance. Distributed Tracing text-generation-inference is instrumented with distributed tracing using OpenTelemetry. You can use this featureby setting the address to an OTLP collector with the --otlp-endpoint argument. Local install You can also opt to install text-generation-inference locally. First install Rust and create a Python virtual environment with at leastPython 3.9, e.g. using conda : ```shellcurl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh conda create -n text-generation-inference python=3.9conda activate text-generation-inference``` You may also need to install Protoc. On Linux: shellPROTOC_ZIP=protoc-21.12-linux-x86_64.zipcurl -OL https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.12/$PROTOC_ZIPsudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local bin/protocsudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local 'include/*'rm -f $PROTOC_ZIP On MacOS, using Homebrew: shellbrew install protobuf Then run: shellBUILD_EXTENSIONS=True make install # Install repository and HF/transformer fork with CUDA kernelsmake run-falcon-7b-instruct Note: on some machines, you may also need the OpenSSL libraries and gcc. On Linux machines, run: shellsudo apt-get install libssl-dev gcc -y CUDA Kernels The custom CUDA kernels are only tested on NVIDIA A100s. If you have any installation or runtime issues, you can removethe kernels by using the DISABLE_CUSTOM_KERNELS=True environment variable. Be aware that the official Docker image has them enabled by default. Run Falcon Run shellmake run-falcon-7b-instruct Quantization You can also quantize the weights with bitsandbytes to reduce the VRAM requirement: shellmake run-falcon-7b-instruct-quantize Develop shellmake server-devmake router-dev Testing ```shell python make python-server-testsmake python-client-tests or both server and client tests make python-tests rust cargo tests make rust-tests integration tests make integration-tests``` Other supported hardware TGI is also supported on the following AI hardware accelerators:- Habana first-gen Gaudi and Gaudi2: checkout here how to serve models with TGI on Gaudi and Gaudi2 with Optimum Habana To restore the repository download the bundle wget https://archive.org/download/github.com-huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42/huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42.bundle and run: git clone huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42.bundle Source: https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference Uploader: huggingface Upload date: 2023-08-01
“Computer Mediated Communication : Computer Conferencing - Electronic Mail, Electronic Publishing - Computer Interviewing, Interactive Text Reading - Group Decision Support Systems, Idea Generation Support Systems, Human Machine Communication, Multi-media Communication, Hypertext - Hypermedia - Linguistic Games : Bibliography” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Computer Mediated Communication : Computer Conferencing - Electronic Mail, Electronic Publishing - Computer Interviewing, Interactive Text Reading - Group Decision Support Systems, Idea Generation Support Systems, Human Machine Communication, Multi-media Communication, Hypertext - Hypermedia - Linguistic Games : Bibliography
- Author: Sabourin, Conrad, 1943-
- Language: English
“Computer Mediated Communication : Computer Conferencing - Electronic Mail, Electronic Publishing - Computer Interviewing, Interactive Text Reading - Group Decision Support Systems, Idea Generation Support Systems, Human Machine Communication, Multi-media Communication, Hypertext - Hypermedia - Linguistic Games : Bibliography” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ Computer networks -- Bibliography - Telematics -- Bibliography
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: computermediated0010sabo
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 1240.75 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 29 times, the file-s went public at Fri May 10 2019.
Available formats:
ACS Encrypted EPUB - ACS Encrypted PDF - Abbyy GZ - Cloth Cover Detection Log - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Dublin Core - EPUB - Item Tile - JPEG Thumb - JSON - LCP Encrypted EPUB - LCP Encrypted PDF - Log - MARC - MARC Binary - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - PNG - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Original JP2 Tar - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - Title Page Detection Log - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Computer Mediated Communication : Computer Conferencing - Electronic Mail, Electronic Publishing - Computer Interviewing, Interactive Text Reading - Group Decision Support Systems, Idea Generation Support Systems, Human Machine Communication, Multi-media Communication, Hypertext - Hypermedia - Linguistic Games : Bibliography at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
38Lexical Semantics And Knowledge Representation In Multilingual Text Generation
By Stede, Manfred, 1965-
Large Language Model Text Generation Inference # Text Generation Inference A Rust, Python and gRPC server for text generation inference. Used in production at [HuggingFace](https://huggingface.co)to power Hugging Chat, the Inference API and Inference Endpoint. Table of contents Features Optimized Architectures Get Started Docker API Documentation Using a private or gated model A note on Shared Memory Distributed Tracing Local Install CUDA Kernels Run Falcon Run Quantization Develop Testing Other supported hardware Features Serve the most popular Large Language Models with a simple launcher Tensor Parallelism for faster inference on multiple GPUs Token streaming using Server-Sent Events (SSE) Continuous batching of incoming requests for increased total throughput Optimized transformers code for inference using flash-attention and Paged Attention on the most popular architectures Quantization with bitsandbytes and GPT-Q Safetensors weight loading Watermarking with A Watermark for Large Language Models Logits warper (temperature scaling, top-p, top-k, repetition penalty, more details see transformers.LogitsProcessor ) Stop sequences Log probabilities Production ready (distributed tracing with Open Telemetry, Prometheus metrics) Optimized architectures BLOOM FLAN-T5 Galactica GPT-Neox Llama OPT SantaCoder Starcoder Falcon 7B Falcon 40B MPT Llama V2 Other architectures are supported on a best effort basis using: AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto") or AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(<model>, device_map="auto") Get started Docker The easiest way of getting started is using the official Docker container: ```shellmodel=tiiuae/falcon-7b-instructvolume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every run docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.0 --model-id $model``` Note: To use GPUs, you need to install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit . We also recommend using NVIDIA drivers with CUDA version 11.8 or higher. To see all options to serve your models (in the code or in the cli: text-generation-launcher --help You can then query the model using either the /generate or /generate_stream routes: shellcurl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate \ -X POST \ -d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' shellcurl 127.0.0.1:8080/generate_stream \ -X POST \ -d '{"inputs":"What is Deep Learning?","parameters":{"max_new_tokens":20}}' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' or from Python: shellpip install text-generation ```pythonfrom text_generation import Client client = Client("http://127.0.0.1:8080")print(client.generate("What is Deep Learning?", max new tokens=20).generated_text) text = ""for response in client.generate stream("What is Deep Learning?", max new_tokens=20): if not response.token.special: text += response.token.textprint(text)``` API documentation You can consult the OpenAPI documentation of the text-generation-inference REST API using the /docs route.The Swagger UI is also available at: https://huggingface.github.io/text-generation-inference . Using a private or gated model You have the option to utilize the HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN environment variable for configuring the token employed by text-generation-inference . This allows you to gain access to protected resources. For example, if you want to serve the gated Llama V2 model variants: Go to https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens Copy your cli READ token Export HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=<your cli READ token> or with Docker: ```shellmodel=meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hfvolume=$PWD/data # share a volume with the Docker container to avoid downloading weights every runtoken= docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -e HUGGING FACE HUB_TOKEN=$token -p 8080:80 -v $volume:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:1.0.0 --model-id $model``` A note on Shared Memory (shm) <code>NCCL</code> is a communication framework used by PyTorch to do distributed training/inference. text-generation-inference makeuse of NCCL to enable Tensor Parallelism to dramatically speed up inference for large language models. In order to share data between the different devices of a NCCL group, NCCL might fall back to using the host memory ifpeer-to-peer using NVLink or PCI is not possible. To allow the container to use 1G of Shared Memory and support SHM sharing, we add --shm-size 1g on the above command. If you are running text-generation-inference inside Kubernetes . You can also add Shared Memory to the container bycreating a volume with: yaml- name: shm emptyDir: medium: Memory sizeLimit: 1Gi and mounting it to /dev/shm . Finally, you can also disable SHM sharing by using the NCCL_SHM_DISABLE=1 environment variable. However, note thatthis will impact performance. Distributed Tracing text-generation-inference is instrumented with distributed tracing using OpenTelemetry. You can use this featureby setting the address to an OTLP collector with the --otlp-endpoint argument. Local install You can also opt to install text-generation-inference locally. First install Rust and create a Python virtual environment with at leastPython 3.9, e.g. using conda : ```shellcurl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh conda create -n text-generation-inference python=3.9conda activate text-generation-inference``` You may also need to install Protoc. On Linux: shellPROTOC_ZIP=protoc-21.12-linux-x86_64.zipcurl -OL https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.12/$PROTOC_ZIPsudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local bin/protocsudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local 'include/*'rm -f $PROTOC_ZIP On MacOS, using Homebrew: shellbrew install protobuf Then run: shellBUILD_EXTENSIONS=True make install # Install repository and HF/transformer fork with CUDA kernelsmake run-falcon-7b-instruct Note: on some machines, you may also need the OpenSSL libraries and gcc. On Linux machines, run: shellsudo apt-get install libssl-dev gcc -y CUDA Kernels The custom CUDA kernels are only tested on NVIDIA A100s. If you have any installation or runtime issues, you can removethe kernels by using the DISABLE_CUSTOM_KERNELS=True environment variable. Be aware that the official Docker image has them enabled by default. Run Falcon Run shellmake run-falcon-7b-instruct Quantization You can also quantize the weights with bitsandbytes to reduce the VRAM requirement: shellmake run-falcon-7b-instruct-quantize Develop shellmake server-devmake router-dev Testing ```shell python make python-server-testsmake python-client-tests or both server and client tests make python-tests rust cargo tests make rust-tests integration tests make integration-tests``` Other supported hardware TGI is also supported on the following AI hardware accelerators:- Habana first-gen Gaudi and Gaudi2: checkout here how to serve models with TGI on Gaudi and Gaudi2 with Optimum Habana To restore the repository download the bundle wget https://archive.org/download/github.com-huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42/huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42.bundle and run: git clone huggingface-text-generation-inference_-_2023-08-01_15-05-42.bundle Source: https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference Uploader: huggingface Upload date: 2023-08-01
“Lexical Semantics And Knowledge Representation In Multilingual Text Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Lexical Semantics And Knowledge Representation In Multilingual Text Generation
- Author: Stede, Manfred, 1965-
- Language: English
“Lexical Semantics And Knowledge Representation In Multilingual Text Generation” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ Computational linguistics - Semantics -- Data processing - Knowledge representation (Information theory)
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: lexicalsemantics0000sted
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 519.89 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 18 times, the file-s went public at Wed May 05 2021.
Available formats:
ACS Encrypted PDF - Cloth Cover Detection Log - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Dublin Core - EPUB - Item Tile - JPEG Thumb - JSON - LCP Encrypted EPUB - LCP Encrypted PDF - Log - MARC - MARC Binary - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - PNG - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Original JP2 Tar - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - Title Page Detection Log - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Lexical Semantics And Knowledge Representation In Multilingual Text Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
39DTIC ADA128194: An Overview Of The Penman Text Generation System.
By Defense Technical Information Center
The problem of programming computers to produce natural language explanations and other texts on demand is an active research area in artifical intelligence. In the past, research systems designed for this purpose have been limited by the weakness of their linguistic bases, especially their grammars, and their techniques often cannot be transferred to new knowledge domains. A new text generation system, Penman, is designed to overcome these problems and produce fluent multiparagraph text in English in response to a goal presented to the system. Penman consists of four major modules: a knowledge acquisition module which can perform domain-specific searches for knowledge relevant to a given communication goal; a text planning module which can organize the relevant information, decide what portion to present, and decide how to lead the reader's attention and knowledge through the content; a sentence generation module based on a large systemic grammar of English; and an evaluation and plan-perturbation module which revises text plans based on evaluation of text produced. Development of Penman has included implementation of the largest systemic grammar of English in a single notation. A new semantic notation has been added to the systemic framework, and the semantics of nearly the entire grammar has been defined. The semantics is designed to be independent of the system's knowledge notation, so that it is usable with widely differing knowledge representtions, including both frame-based and predicate-calculus-based approaches. (Author)
“DTIC ADA128194: An Overview Of The Penman Text Generation System.” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA128194: An Overview Of The Penman Text Generation System.
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA128194: An Overview Of The Penman Text Generation System.” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Mann,William C - UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA MARINA DEL REY INFORMATION SCIENCES INST - *COMPUTER APPLICATIONS - *ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE - *SYSTEMS APPROACH - *TEXT PROCESSING - SYSTEMS ENGINEERING - COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN - SEMANTICS - FLOW CHARTING - MAN COMPUTER INTERFACE - COMPUTATIONAL LINGUISTICS - LINGUISTICS - GRAMMARS - ENGLISH LANGUAGE
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA128194
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 10.35 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 90 times, the file-s went public at Thu Jan 11 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA128194: An Overview Of The Penman Text Generation System. at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
40A Hybrid Convolutional Variational Autoencoder For Text Generation
By Stanislau Semeniuta, Aliaksei Severyn and Erhardt Barth
In this paper we explore the effect of architectural choices on learning a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) for text generation. In contrast to the previously introduced VAE model for text where both the encoder and decoder are RNNs, we propose a novel hybrid architecture that blends fully feed-forward convolutional and deconvolutional components with a recurrent language model. Our architecture exhibits several attractive properties such as faster run time and convergence, ability to better handle long sequences and, more importantly, it helps to avoid some of the major difficulties posed by training VAE models on textual data.
“A Hybrid Convolutional Variational Autoencoder For Text Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ A Hybrid Convolutional Variational Autoencoder For Text Generation
- Authors: Stanislau SemeniutaAliaksei SeverynErhardt Barth
“A Hybrid Convolutional Variational Autoencoder For Text Generation” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-1702.02390
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 0.61 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 34 times, the file-s went public at Sat Jun 30 2018.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Metadata - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find A Hybrid Convolutional Variational Autoencoder For Text Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
41Microsoft Research Video 104302: Enhancing Text Representation Through Knowledge-Based Feature Generation
By Microsoft Research
Imagine an automatic news filtering system that tracks company news. Given the news item 'FDA approves ciprofloxacin for victims of anthrax inhalation', how can the system know that the drug mentioned is an antibiotic produced by Bayer? Or consider an information professional searching for data on RFID technology - how can a computer understand that the item 'Wal-Mart supply chain goes real time' is relevant for the search? Algorithms we present can do just that. When humans approach text processing tasks, such as text categorization, they interpret documents in the context of their background knowledge and experience. On the other hand, conventional information retrieval systems represent documents as bags of words, and are restricted to learning from individual word occurrences in the (necessarily limited) training set. We propose to enrich document representation through automatic use of vast repositories of human knowledge. To this end, we use knowledge concepts derived from the Open Directory Project and Wikipedia, the largest Web directory and encyclopedia, respectively. In the preprocessing phase, a feature generator analyzes the input documents and maps them onto relevant concepts. The latter give rise to a set of generated features that augment the standard bag of words. Feature generation is accomplished through contextual analysis of document text, thus implicitly performing word sense disambiguation. Coupled with the ability to generalize from words to concepts, this approach addresses the two main problems of natural language processing synonymy and polysemy. Categorizing documents with the aid of knowledge-based features leverages information that cannot be deduced from the training documents alone. Empirical results confirm that this knowledge-intensive representation brings text categorization to a qualitatively new level of performance across a diverse collection of datasets. We also propose a new, knowledge-based approach for computing the degree of semantic relatedness of texts. ©2006 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
“Microsoft Research Video 104302: Enhancing Text Representation Through Knowledge-Based Feature Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Microsoft Research Video 104302: Enhancing Text Representation Through Knowledge-Based Feature Generation
- Author: Microsoft Research
- Language: English
“Microsoft Research Video 104302: Enhancing Text Representation Through Knowledge-Based Feature Generation” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ Microsoft Research - Microsoft Research Video Archive - Paul Viola - Evgeniy Gabrilovich
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ➤ Microsoft_Research_Video_104302
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "movies" format, the size of the file-s is: 1072.63 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 59 times, the file-s went public at Thu May 01 2014.
Available formats:
Animated GIF - Archive BitTorrent - Item Tile - Metadata - Ogg Video - Thumbnail - Windows Media - h.264 -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Microsoft Research Video 104302: Enhancing Text Representation Through Knowledge-Based Feature Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
42DTIC ADA148990: Cohesion In Computer Text Generation: Lexical Substitution.
By Defense Technical Information Center
This report describes Paul, a computer text generation system designed to create cohesive text. The device used to achieve this cohesion is lexical substitution. Through the use of syntactic and semantic information, the system is able to determine which type of lexical substitution will provide the necessary information to generate an understandable reference, while not providing so much information that the reference is confusing or unnatural. Specifically, Paul is designed to deterministically choose between pronominalization, superordinate substitutions, and definite noun phrase reiteration. The system identifies a strength of antecedence recovery for each of the lexical substitutions, and matches them against the strength of potential antecedence of each element in the text to select the proper substitutions for these elements. There are five classes of potential antecedence based on the element's current and previous syntactic roles, semantic case roles, and the current focus of the discourse. Through the use of these lexial substitutions, Paul is able able to generate a cohesive text which exhibits the binding of sentences through presupposition dependencies, the marking of old information from new, and the avoiding of unnecessary and tedious repetitions.
“DTIC ADA148990: Cohesion In Computer Text Generation: Lexical Substitution.” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA148990: Cohesion In Computer Text Generation: Lexical Substitution.
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA148990: Cohesion In Computer Text Generation: Lexical Substitution.” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Granville,R A - MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH CAMBRIDGE LAB FOR COMPUTER SCIENCE - *TEXT PROCESSING - COMPUTER APPLICATIONS
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA148990
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 96.22 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 158 times, the file-s went public at Sat Jan 27 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA148990: Cohesion In Computer Text Generation: Lexical Substitution. at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
43DTIC ADA214273: Knowledge Based Text Generation
By Defense Technical Information Center
This report develops a theory of text generation and describes an implemented computational model of this theory. The theory attempts both domain independency at the knowledge level and language independency at the linguistic level by drawing and expanding upon previous work in discourse schema and grammatical relations, respectively. The implemented system, GENNY, generates coherent texts by employing discourse strategies (which occur in human produced text) in parallel with pragmatic constraints (e.g., focus and context). The report begins with an introduction and summary of the research performed. This is followed by a survey of the text generation literature which places GENNY in the context of past language production research. Next, the motivation for the theoretical position adopted is discussed followed by detail of the theory on a knowledge, pragmatic, semantic, relational, and syntactic level, with illustration of the practical implementation throughout. Results of GENNY's test production from two frame knowledge bases (neuropsychology and photography) are then presented together with preliminary interlingual test results (English and Italian). GENNY is evaluated with respect to state-of-the-art generators and is shown to be equivalent and, in some respects, superior, in competence and performance. In conclusion, the contributions and limitations of the system are discussed for further development are suggested. Keywords: Natural language generation. (kr)
“DTIC ADA214273: Knowledge Based Text Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA214273: Knowledge Based Text Generation
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA214273: Knowledge Based Text Generation” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Maybury, Mark T - ROME AIR DEVELOPMENT CENTER GRIFFISS AFB NY - *TEXT PROCESSING - *NATURAL LANGUAGE - PRODUCTION - STATE OF THE ART - COHERENCE - LIMITATIONS - PHOTOGRAPHY - FRAMES - MOTIVATION - GENERATORS - ENGINEERING DRAWINGS - SYNTAX - LINGUISTICS - COMPUTATIONS - TEST AND EVALUATION - MATHEMATICAL MODELS
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA214273
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 68.97 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 73 times, the file-s went public at Fri Feb 23 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA214273: Knowledge Based Text Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
44RTP Payload Format For 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Timed Text
By J. Rey and Y. Matsui
This document specifies an RTP payload format for the transmission of 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) timed text. 3GPP timed text is a time-lined, decorated text media format with defined storage in a 3GP file. Timed Text can be synchronized with audio/video contents and used in applications such as captioning, titling, and multimedia presentations. In the following sections, the problems of streaming timed text are addressed, and a payload format for streaming 3GPP timed text over RTP is specified. [STANDARDS-TRACK]
“RTP Payload Format For 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Timed Text” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ RTP Payload Format For 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Timed Text
- Authors: J. ReyY. Matsui
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: rfc4396
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 31.57 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 74 times, the file-s went public at Tue Jan 24 2023.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - HTML - Item Tile - JSON - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find RTP Payload Format For 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Timed Text at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
45DTIC ADA460211: An Object Oriented Approach To Content Planning For Text Generation
By Defense Technical Information Center
This paper describes GENIE, an object-oriented architecture that generates text with the intent of extending user expertise in interactive environments. Such environments present three interesting goals. First, to provide information within the task at hand. Second to both respond to a user's task related question and simultaneously extend their knowledge. Third, to do this in a manner that is concise, clear and cohesive. Instead of generating text based solely on either discourse goals, intentions, or the domain, we found a need to combine techniques from each. We have developed an object oriented architecture in which the concepts about which we talk (domain entities), the goals that may be accomplished with them (intentions), end the rhetorical acts through which we express them (discourse goals) are represented as objects with localized knowledge end methods. This paper describes how current text planning methods were insufficient for our needs, and presents our object-oriented method as an alternative.
“DTIC ADA460211: An Object Oriented Approach To Content Planning For Text Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DTIC ADA460211: An Object Oriented Approach To Content Planning For Text Generation
- Author: ➤ Defense Technical Information Center
- Language: English
“DTIC ADA460211: An Object Oriented Approach To Content Planning For Text Generation” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ DTIC Archive - Wolz, Ursula - COLUMBIA UNIV NEW YORK DEPT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE - *OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING - COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE - PLANNING - KNOWLEDGE BASED SYSTEMS
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: DTIC_ADA460211
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 13.20 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 47 times, the file-s went public at Fri Jun 08 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - JPEG Thumb - Metadata - OCR Page Index - OCR Search Text - Page Numbers JSON - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF - chOCR - hOCR -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DTIC ADA460211: An Object Oriented Approach To Content Planning For Text Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
46Privacy-Preserving Population-Enhanced Biometric Key Generation From Free-Text Keystroke Dynamics
By Jaroslav Sedenka, Kiran Balagani, Vir Phoha and Paolo Gasti
Biometric key generation techniques are used to reliably generate cryptographic material from biometric signals. Existing constructions require users to perform a particular activity (e.g., type or say a password, or provide a handwritten signature), and are therefore not suitable for generating keys continuously. In this paper we present a new technique for biometric key generation from free-text keystroke dynamics. This is the first technique suitable for continuous key generation. Our approach is based on a scaled parity code for key generation (and subsequent key reconstruction), and can be augmented with the use of population data to improve security and reduce key reconstruction error. In particular, we rely on linear discriminant analysis (LDA) to obtain a better representation of discriminable biometric signals. To update the LDA matrix without disclosing user's biometric information, we design a provably secure privacy-preserving protocol (PP-LDA) based on homomorphic encryption. Our biometric key generation with PP-LDA was evaluated on a dataset of 486 users. We report equal error rate around 5% when using LDA, and below 7% without LDA.
“Privacy-Preserving Population-Enhanced Biometric Key Generation From Free-Text Keystroke Dynamics” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Privacy-Preserving Population-Enhanced Biometric Key Generation From Free-Text Keystroke Dynamics
- Authors: Jaroslav SedenkaKiran BalaganiVir PhohaPaolo Gasti
“Privacy-Preserving Population-Enhanced Biometric Key Generation From Free-Text Keystroke Dynamics” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-1407.4179
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 0.18 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 43 times, the file-s went public at Sat Jun 30 2018.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Metadata - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Privacy-Preserving Population-Enhanced Biometric Key Generation From Free-Text Keystroke Dynamics at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
47Transitive Text Mining For Information Extraction And Hypothesis Generation
By Johannes Stegmann and Guenter Grohmann
Transitive text mining - also named Swanson Linking (SL) after its primary and principal researcher - tries to establish meaningful links between literature sets which are virtually disjoint in the sense that each does not mention the main concept of the other. If successful, SL may give rise to the development of new hypotheses. In this communication we describe our approach to transitive text mining which employs co-occurrence analysis of the medical subject headings (MeSH), the descriptors assigned to papers indexed in PubMed. In addition, we will outline the current state of our web-based information system which will enable our users to perform literature-driven hypothesis building on their own.
“Transitive Text Mining For Information Extraction And Hypothesis Generation” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Transitive Text Mining For Information Extraction And Hypothesis Generation
- Authors: Johannes StegmannGuenter Grohmann
- Language: English
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-cs0509020
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 4.25 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 75 times, the file-s went public at Wed Sep 18 2013.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Animated GIF - Archive BitTorrent - DjVu - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Transitive Text Mining For Information Extraction And Hypothesis Generation at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
48Dynamics Of Text Generation With Realistic Zipf Distribution
By Damián H. Zanette and Marcelo A. Montemurro
We investigate the origin of Zipf's law for words in written texts by means of a stochastic dynamical model for text generation. The model incorporates both features related to the general structure of languages and memory effects inherent to the production of long coherent messages in the communication process. It is shown that the multiplicative dynamics of our model leads to rank-frequency distributions in quantitative agreement with empirical data. Our results give support to the linguistic relevance of Zipf's law in human language.
“Dynamics Of Text Generation With Realistic Zipf Distribution” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Dynamics Of Text Generation With Realistic Zipf Distribution
- Authors: Damián H. ZanetteMarcelo A. Montemurro
- Language: English
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-cond-mat0212496
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 3.46 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 97 times, the file-s went public at Wed Sep 18 2013.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Animated GIF - Archive BitTorrent - DjVu - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - JPEG Thumb - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Dynamics Of Text Generation With Realistic Zipf Distribution at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
49DeepText: A Unified Framework For Text Proposal Generation And Text Detection In Natural Images
By Zhuoyao Zhong, Lianwen Jin, Shuye Zhang and Ziyong Feng
In this paper, we develop a novel unified framework called DeepText for text region proposal generation and text detection in natural images via a fully convolutional neural network (CNN). First, we propose the inception region proposal network (Inception-RPN) and design a set of text characteristic prior bounding boxes to achieve high word recall with only hundred level candidate proposals. Next, we present a powerful textdetection network that embeds ambiguous text category (ATC) information and multilevel region-of-interest pooling (MLRP) for text and non-text classification and accurate localization. Finally, we apply an iterative bounding box voting scheme to pursue high recall in a complementary manner and introduce a filtering algorithm to retain the most suitable bounding box, while removing redundant inner and outer boxes for each text instance. Our approach achieves an F-measure of 0.83 and 0.85 on the ICDAR 2011 and 2013 robust text detection benchmarks, outperforming previous state-of-the-art results.
“DeepText: A Unified Framework For Text Proposal Generation And Text Detection In Natural Images” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ DeepText: A Unified Framework For Text Proposal Generation And Text Detection In Natural Images
- Authors: Zhuoyao ZhongLianwen JinShuye ZhangZiyong Feng
“DeepText: A Unified Framework For Text Proposal Generation And Text Detection In Natural Images” Subjects and Themes:
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: arxiv-1605.07314
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 0.87 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 35 times, the file-s went public at Fri Jun 29 2018.
Available formats:
Archive BitTorrent - Metadata - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find DeepText: A Unified Framework For Text Proposal Generation And Text Detection In Natural Images at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
50Narrative: Text Generation Model From Data
By Darío Arenas, Javier Pérez, David Martínez,David Llorente, Eugenio Fernández, Antonio Moratilla
The generation of digital content has undergone a great increase in recent years due to the development of new technologies that allow the creation of content quickly and easily. A further step in this evolution is the generation of contents by automatic systems without human intervention. Thus, for decadesit has been developing models for the Natural Language Generation (NLG) that allow the transformation of content to the form of narratives. At present, there are several systems that enable the generation in text format. In this paper we present the Narrative system, which allows the generation of text narratives from different sources, and which are indistinguishable for user from those made by a human being.
“Narrative: Text Generation Model From Data” Metadata:
- Title: ➤ Narrative: Text Generation Model From Data
- Author: ➤ Darío Arenas, Javier Pérez, David Martínez,David Llorente, Eugenio Fernández, Antonio Moratilla
- Language: English
“Narrative: Text Generation Model From Data” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: ➤ Automatic Digital Content Generation - D2T - NLG
Edition Identifiers:
- Internet Archive ID: ➤ Httpwww.ijmret.orgpaperV2I802082027.pdf
Downloads Information:
The book is available for download in "texts" format, the size of the file-s is: 6.29 Mbs, the file-s for this book were downloaded 123 times, the file-s went public at Sun Aug 12 2018.
Available formats:
Abbyy GZ - Archive BitTorrent - DjVuTXT - Djvu XML - Item Tile - Metadata - Scandata - Single Page Processed JP2 ZIP - Text PDF -
Related Links:
- Whefi.com: Download
- Whefi.com: Review - Coverage
- Internet Archive: Details
- Internet Archive Link: Downloads
Online Marketplaces
Find Narrative: Text Generation Model From Data at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
Source: The Open Library
The Open Library Search Results
Available books for downloads and borrow from The Open Library
1Generation text
By Michael M. Osit

“Generation text” Metadata:
- Title: Generation text
- Author: Michael M. Osit
- Language: English
- Number of Pages: Median: 276
- Publisher: ➤ AMACOM - American Management Association - AMACOM Books
- Publish Date: 2008 - 2009
- Publish Location: New York
“Generation text” Subjects and Themes:
- Subjects: Technology and children - Child rearing - Family & Relationships - Nonfiction
Edition Identifiers:
- The Open Library ID: OL24270021M - OL18534447M
- Online Computer Library Center (OCLC) ID: 214935076
- Library of Congress Control Number (LCCN): 2008013544
- All ISBNs: 9780814410868 - 0814409326 - 9780814409329 - 0814410863
Access and General Info:
- First Year Published: 2008
- Is Full Text Available: Yes
- Is The Book Public: No
- Access Status: Borrowable
Online Access
Downloads Are Not Available:
The book is not public therefore the download links will not allow the download of the entire book, however, borrowing the book online is available.
Online Borrowing:
- Borrowing from Open Library: Borrowing link
- Borrowing from Archive.org: Borrowing link
Online Marketplaces
Find Generation text at online marketplaces:
- Amazon: Audiable, Kindle and printed editions.
- Ebay: New & used books.
Buy “Generation Text” online:
Shop for “Generation Text” on popular online marketplaces.
- Ebay: New and used books.